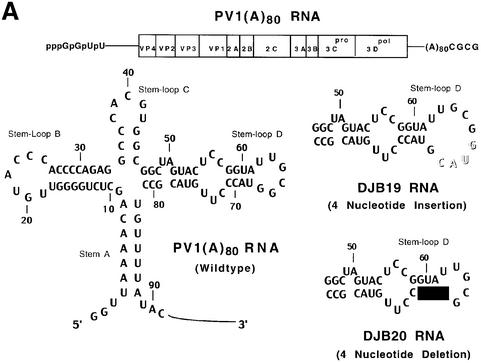
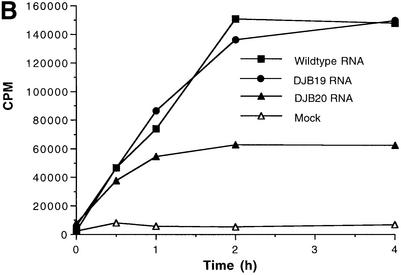
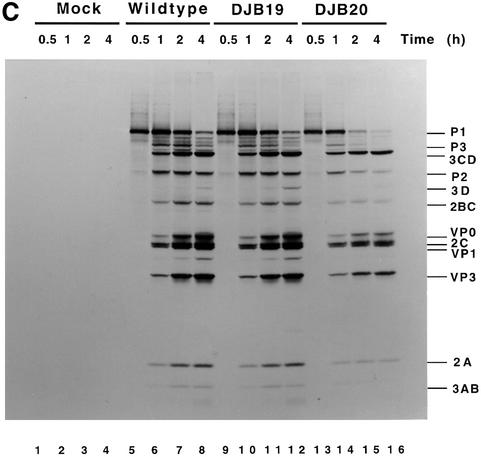
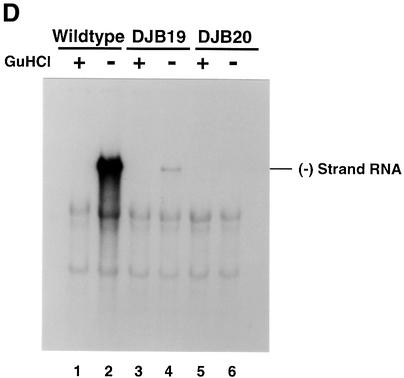
Fig. 1. Effect of 5′ cloverleaf mutations on viral protein synthesis and negative-strand RNA synthesis. (A) Diagram of poliovirus transcript RNA, T7-PV1(A)80 RNA, and 5′ cloverleaf structure. The wild-type cloverleaf structure, the GUAC insertion in stem–loop D in DJB19 RNA and the GUAC deletion (black box) in stem–loop D in DJB20 RNA are shown. (B) Viral protein synthesis was measured in HeLa S10 in vitro translation–replication reactions containing either T7-PV1(A)80 RNA (wild type), DJB19 RNA or DJB20 RNA. The translation reactions contained [35S]methionine (1.2 mCi/ml) and 50 µg/ml RNA as indicated. At the indicated times, 1 µl samples were removed from each reaction. The labeled viral proteins were precipitated in 5% trichloroacetic acid, collected on filters and quantitated by scintillation counting. The amount of labeled protein synthesized in each reaction was plotted as a function of reaction time. (C) SDS–PAGE analysis of the labeled viral proteins. At the indicated times, 4 µl samples were removed from each translation reaction. The labeled viral proteins were solubilized in 50 µl of SDS sample buffer, denatured at 100°C for 3 min and 20 µl portions were separated by electrophoresis in an SDS–9–18% polyacrylamide gel. The gel was fixed and fluorographed. (D) Negative-strand RNA synthesis was measured using preinitiation RNA replication complexes isolated from HeLa S10 translation–RNA replication reactions containing guanidine HCL and each of the indicated RNAs using the procedures described in Materials and methods. Reactions containing the preinitiation RNA replication complexes were incubated at 37°C for 32 min and 32P-labeled negative-strand RNA was fractionated by CH3HgOH–agarose gel electrophoresis. The position of poliovirus negative-strand RNA is indicated.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.