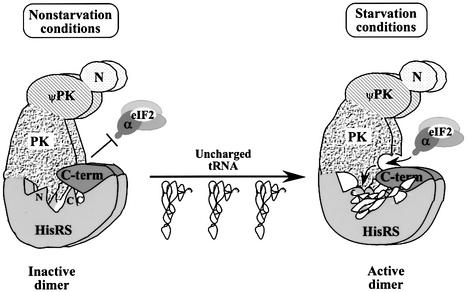
Fig. 8. A model depicting allosteric alterations in domain interactions in GCN2 elicited by bound tRNA that result in kinase activation. The domains of GCN2 are labeled as follows: binding domain for GCN1–GCN20 complex at the N-terminus, N; pseudokinase domain, ψPK; protein kinase domain, PK; HisRS-like region, HisRS; and C-term. The N- and C-terminal portions of the HisRS domain (labeled N and C in the HisRS region of the schematic on the left) interact with the PK and C-term segments, respectively. In the inactive form of GCN2 present in non-starvation conditions (left), productive association with the substrate eIF2 is prevented by binding of the C-term to the PK domain, and possibly also by HisRS-N–PK interactions (both inhibitory interactions are depicted by overlapped domains). The HisRS-N–PK interactions in this state are not compatible with tRNA binding. Under starvation conditions (right), uncharged tRNA binds to GCN2, making contacts with both the HisRS-N and C-term domains. The bound tRNA produces conformational changes in both domains that are transmitted to the PK domain. This opens up the substrate binding cleft in the PK domain and allows eIF2 binding and phosphorylation (the allosteric alteration in the PK domain is signified by the curved arrow in this domain.) The HisRS-N region remains engaged with the PK domain and contributes to its active conformation. The C-term also remains associated with the PK domain, but inhibitory C-term–PK contacts are lost upon tRNA binding. These inhibitory contacts are also weakened by the constitutively activating E803V mutation in the PK domain. Both inactive and active forms of GCN2 are depicted as dimers because GCN2 can dimerize in the absence of an intact HisRS domain and its tRNA binding activity. This model does not depict the potential ‘criss-cross’ interactions that could occur if the C-term of one subunit interacts with the HisRS-C region of the other subunit, as found in the crystal structure of authentic E.coli HisRS (see text for further details).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.