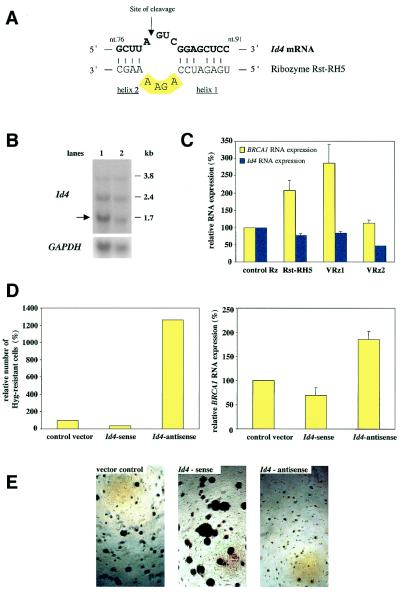
Figure 4.
Identification and validation of Id4 as a negative regulator of the BRCA1 promoter. (A) Schematic illustration of the predicted binding of Rst-RH5 to Id4 mRNA (numbering of Id4 nucleotides according to GenBank accession no. NM 001546). (B) Northern analysis for Id4 RNA in ribozyme-library- (lane 2) or control vector (lane 1)-transduced P8EGBR3 cells after sort #5 (compare with Fig. 2). Different messages result from alternative polyadenylation. The major message is indicated (arrow). (C) Effects of Rst-RH5 and two validation ribozymes (VRz1 or VRz2) on endogenous BRCA1 and Id4 expression measured by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Expression of BRCA1 or Id4 mRNA was normalized to GAPDH mRNA. Numbers are given as relative RNA levels in percent compared with the control ribozyme (mean ± SEM). (D) The Hygromycin B resistance assay. Quantitative analysis of cell survival and of endogenous BRCA1 expression (measured by quantitative real-time RT-PCR and normalized to GAPDH message) in control vector-, Id4-sense-, or Id4-antisense-transduced cells after phenotypic selection of Hygromycin B reporter cells with Hygromycin B. Numbers are given in percent compared with control vector (mean ± SEM). (E) Anchorage-independent growth of P8EGBR3 cells transduced with control vector, Id4-sense, or Id4-antisense expression vectors.