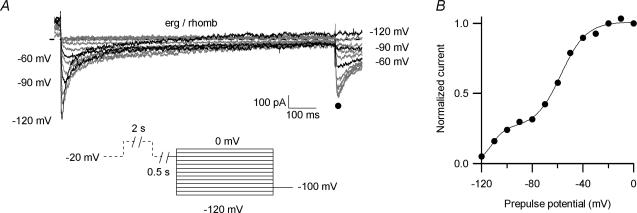
Figure 8. A slowly deactivating erg current component occurs in a subpopulation of rhombencephalon neurones.
Erg current availability measured in an embryonic rhombencephalon neurone using the same pulse protocol as in Fig. 2 (see pulse diagram). A, E-4031-sensitive current from a rhombencephalon neurone with a fast and a slowly deactivating erg current component. Current traces recorded with test pulses to −60, −90 and −120 mV shown in black. B, normalized peak tail current amplitudes of the E-4031-sensitive current shown in A plotted versus prepulse potential. Data points were fitted with the sum of two Boltzmann functions. The slowly deactivating erg current component was described by V1/1=−112 mV and a slope factor of k= 5 mV and the fast deactivating current component by V1/1=−57 mV and a slope factor of 10 mV. The relative contribution of the slowly deactivating current component to the total current amplitude in this neurone was 0.25.