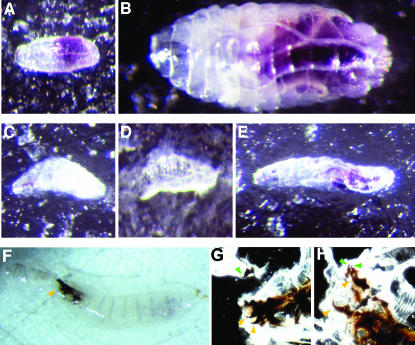
Figure 8.
stv mutants have feeding and molting disabilities. (A and B) stv1/TM6B, Tb germline clone-derived zygotically rescued (m−z+) larvae. (C–E) stv1/stv2 maternal zygotic mutant (m−z−) larvae. (F and G) stv1/stv3 m−z− larvae. All larvae were placed on bromophenol-blue-containing yeast paste <2 hr after hatching. (A and C) Approximately 8 hr after hatching, mutant and zygotically rescued larvae are of a comparable size, although blue food can be seen in the gut of the latter but not the former. (B) By ∼48 hr after hatching, this zygotically rescued larva has grown substantially and completed the first molt, while others progress through the second molt (not shown). (D) In contrast, a stv1/stv2 mutant larva, shown at the same magnification as the heterozygous larva in B, has not grown at all. (E) In contrast to D, this larva has doubled in length since hatching, and some blue dye is visible. However, the size increase is minor compared with the zygotically rescued larva of the same age (B), and no molts have occurred. All larvae are shown at the same magnification. (F–H) A hypomorphic allelic combination does not result in feeding difficulties, but a significant proportion of larvae become stuck at the second molt. (F) An example of a stv1/stv3 larva (m−z−) that has failed to molt correctly between the second and third larval instar. This larva has managed to free itself of its old cuticle, but the cuticle remains attached to the mouth-hook apparatus (arrowhead). (G) Larva shown in F squashed between two microscope slides to visualize the mouth hooks. Both the smaller second instar mouth hooks (green arrowheads) and the third instar mouth hooks (red arrowheads) can be seen, indicating that the cuticle remained attached because the mouth hooks have not resolved. (H) Squash of a second larva, which failed to separate the new and old cuticles. Again, both second and third instar mouth hooks can be seen (green and yellow arrowheads, respectively).