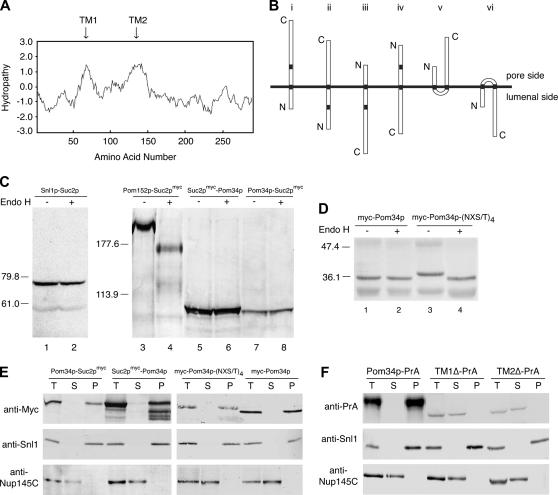
Figure 1.
Pom34p is a double-pass integral membrane protein with the N- and the C-terminal regions exposed to the cytosol/pore. (A) Kyte–Doolittle hydropathy analysis (with a 20-amino-acid window size) (Kyte and Doolittle 1982) of Pom34p revealed two spans (arrows) extending from amino acid residues 64 to 84 (TM1) and 132 to 153 (TM2) with significant hydropathic character and length to be transmembrane segments. (B) Six possible topological models for Pom34p relative to the pore membrane are shown. N, amino; C, carboxy. (C) Cell extracts from strains expressing Snl1p-Suc2p (pSW939) (lanes 1 and 2), Pom152p-Suc2pmyc (pSW3192) (lanes 3 and 4), Suc2pmyc-Pom34p (pSW3189) (lanes 5 and 6), or Pom34p-Suc2pmyc (pSW3190) (lanes 7 and 8) were either mock digested (−) or treated with Endo H (+) and analyzed by immunoblotting using rabbit anti-Snl1p (lanes 1 and 2) or mouse monoclonal 9E10 (anti-c-Myc) (lanes 3–8). Molecular mass markers are indicated in kilodaltons. (D) Four potential N-linked glycosylation sites were generated between TM1 and TM2 of Pom34p by site-directed mutagenesis. Cell extracts from SWY2565 expressing either wild-type myc-Pom34p (lanes 1 and 2) or glycosylation site myc-Pom34p-(NXT/S)4 (lanes 3 and 4) were treated with Endo H as in C. Immunoblotting was conducted with the mouse monoclonal 9E10 (anti-c-Myc) antibody. (E) Spheroplast lysates from the pom34Δ strain expressing Suc2pmyc-Pom34p (pSW3189), Pom34p-Suc2pmyc (pSW3190), wild-type myc-Pom34p (pSW3193), or myc-Pom34p-(NXT/S)4 (pSW3194) were alkali extracted and separated into supernatant (S indicates S1 and S2) and pellet (P indicates P2) fractions by centrifugation. Fractions were analyzed by immunoblotting with the mouse monoclonal 9E10 (anti-Myc), rabbit anti-Snl1p or with rabbit anti-Nup145C antibodies. (F) Spheroplast lysates from pom34Δ cells expressing Pom34p-PrA, TM1Δ-PrA (lacking the TM1), or TM2Δ-PrA (lacking the TM2) were alkali extracted and separated into S and P fractions by centrifugation as in E. Fractions were analyzed by immunoblotting with rabbit anti-mouse (anti-protein A), rabbit anti-Snl1p, or rabbit anti-Nup145C antibodies.