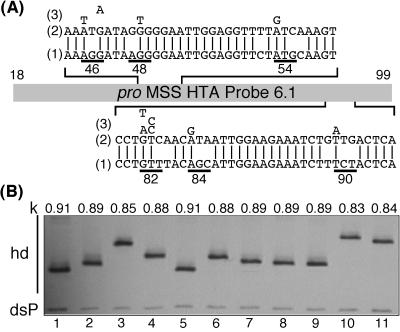
Figure 1.
Characteristics of the pro MSS HTA probe 6.1. (A) Sequence of the probe (1) aligned to the Hxb-2r sequence (2) in the areas of the target positions. Base changes leading to resistance are indicated above the wild-type sequence (3). Resistance-relevant changes are in close proximity to probe wild-type mismatches. (B) Mobility of the radioactively labeled probe annealed to PCR products of pro genes with point mutations. Only the heteroduplexes (hd) and the probe that annealed to its fully complementary strand (double-stranded probe, dsP) are shown. Lanes: 1, wild type; 2, M46I; 3, G48V; 4, I54T; 5, L63P; 6, V82T; 7, V82A; 8, I84V; 9, L90M; 10, G48V/V82T; and 11, G48V/L90M. The mobility (k) of each hd relative to the dsP is indicated above all lanes. Note that wild type and L63P, a nontargeted mutation, have identical mobilities, whereas all of the targeted mutations display lower mobilities. The mobilities of the hds are calculated relative to the dsP to control for differences in the gel or in the electric field between lanes and gels.