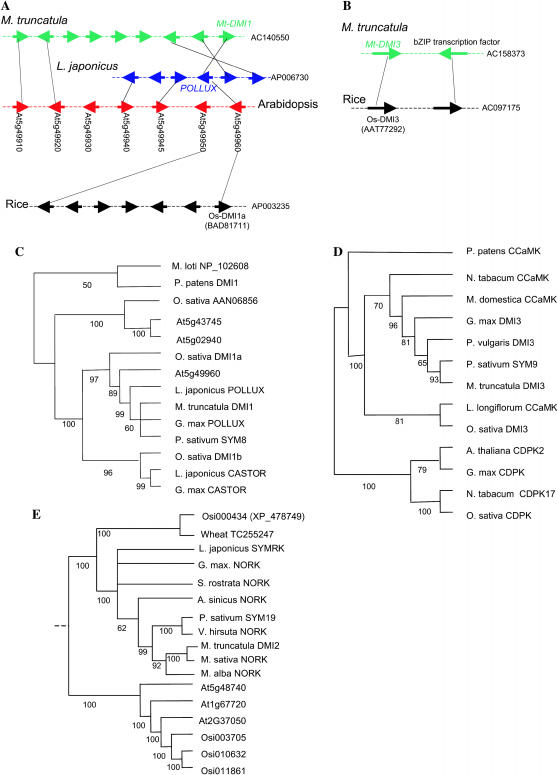
Figure 3.
Microsynteny and phylogeny of DMI homologs in M. truncatula, L. japonicus, rice, and Arabidopsis. Trees (C, D, and E) are strict consensus from the most parsimonious (MP) trees. The numbers of MP trees found were five (C), four (E), and one (D). Numbers below the branches represent the percentages of 500 bootstrap replications supporting the particular nodes. The strict consensus tree of DMI1 homologs (C) was rooted using the bacterial Mesorhizobium loti and the moss P. patens homologs. The strict consensus tree of DMI2-like proteins (E) was rooted according to Shiu et al. (2004). The strict consensus tree of calcium- and calmodulin-dependent kinases (CCaMKs) (D) was rooted using the closest calcium-dependent kinase (CDPK) sequences.