TABLE 4.
QTL affecting variation in pigmentation between D. yakuba and D. santomea
| Backcross population | Sex | QTL | Peak LRa | LRa | Effect (SE)b | Effect/σpc | R2d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 females × D. yakuba males | F | 1A5–13E1 | 1A5 | 26.71 | 0.68 (0.18) | 0.31 | 0.0169 |
| 15F4–20E | 8E10 | 87.08 | 1.44 (0.56) | 0.66 | 0.0584 | ||
| 34B4–57E6 | 34B4 | 441.74 | 1.81 (0.76) | 0.83 | 0.4382 | ||
| 69A1–83C4 | 80B2 | 130.57 | 1.69 (0.69) | 0.78 | 0.1135 | ||
| M | 1A5–13E1 | 3B1-2 | 65.13 | 2.60 (0.65) | 0.62 | 0.0327 | |
| 15F4–20E | 17D6 | 525.94 | 6.75 (2.24) | 1.62 | 0.3186 | ||
| 34B4–57E6 | 34B4 | 193.19 | 3.29 (0.70) | 0.79 | 0.1060 | ||
| 69A1–83C4 | 80B2 | 216.23 | 3.51 (0.91) | 0.84 | 0.1227 | ||
| F1 females × D. santomea males | F | 15F4–20E | 19C1 | 53.485 | −1.39 (0.68) | −1.27 | 0.4280 |
| M | 1A5–13E1 | 1A5 | 67.88 | −2.16 (0.45) | −0.61 | 0.0409 | |
| 15F4–20E | 17D6 | 450.81 | −5.03 (1.84) | −1.42 | 0.3964 | ||
| 34B4–57E6 | 34B4 | 199.18 | −1.73 (0.61) | −0.49 | 0.1397 | ||
| 69A1–83C4 | 80B2 | 133.46 | −2.72 (0.76) | −0.77 | 0.0966 |
QTL regions are estimated from 2 LOD support intervals (P ≤ 0.05). The peak is the cytological location with the highest likelihood ratio (LR). Cytological locations are given on the basis of D. melanogaster cytology (Lemeunier and Ashburner 1976).
Effects were estimated from the least-squares means of the two marker locus classes as: 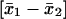 , where the subscript is 1 if the marker has a homozygous genotype and 2 if the marker has a heterozygous or hemizygous genotype. The standard error (SE) is listed in parentheses.
, where the subscript is 1 if the marker has a homozygous genotype and 2 if the marker has a heterozygous or hemizygous genotype. The standard error (SE) is listed in parentheses.
Effect divided by the phenotypic standard deviation. See footnote a for the calculation of the effect.
The proportion of variance explained by the QTL and estimated by 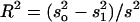 , where s2 is the variance of the trait,
, where s2 is the variance of the trait,  is the sample variance of the residuals, and
is the sample variance of the residuals, and 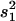 is the variance of the residuals (Basten et al. 1999).
is the variance of the residuals (Basten et al. 1999).
