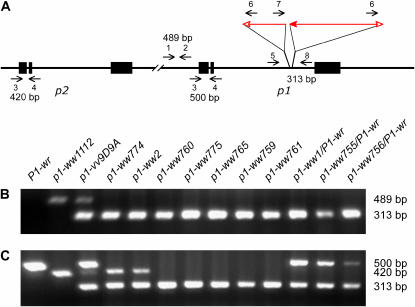
Figure 2.
Detection of deletions by PCR analysis. (A) Structure of the p1-vv9D9A haplotype, including p1 (right) and its paralog p2 (left). Symbols have the same meaning as in Figure 1. Short horizontal arrows indicate the orientations and approximate positions of the primers used in PCR analysis. (B) Screening for deletions of sequences 5′ of the p1 gene using primer pair p1-1 + p1-2, which gives a 489-bp product in p1-vv9D9A. The primer pair Ac-6 + p1-8 detects a 313-bp band from the junction of the 3′-end of Ac with the 3′ sequence of p1 intron 2. PCR was performed using genomic DNA from plants of the genotypes indicated above each lane. The lane marked P1-wr contains DNA from the W22 inbred. The P1-wr allele has been previously shown to contain a tandem array of p1 genes (Chopra et al. 1998), whereas no p2 gene was detected in 16 diverse maize inbred lines containing P1-wr (Szalma et al. 2005). The negative result in the P1-wr lane would suggest that P1-wr alleles also lack (or are polymorphic for) the sequence upstream of p1 in p1-vv. The p1-ww1112 allele contains a deletion of p1 (Athma and Peterson 1991) and retains the p2 gene (Zhang et al. 2000). (C) Screening for deletions of the 5′-end of the p2 gene using primer pair p1-3 + p1-4, which gives a 420-bp product from the p2 gene and a 500-bp product from the p1 gene. As in B, primer pair Ac-6 + p1-8 detects a 313-bp band derived from the junction of the 3′-end of Ac with the 3′ sequence of p1 intron 2.