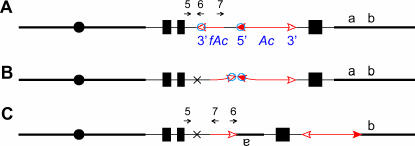
Figure 6.
Hypothetical transposition involving the fAc 3′-end and the Ac 5′-end on the same chromatid in p1-vv9D9A (symbols have the same meaning as in Figure 1). This type of transposition reaction would result in reorientation of the sequences hybridizing to oligonucleotide primers 6 (Ac-6) and 7 (Ac-7) (compare A and C) and thus could be detected by PCR. No such products were detected among 10 p1-ww alleles tested. See text for details. (A) Ac transposase binds to a fAc 3′-end and an Ac 5′-end in the same chromatid. (B) Cuts are made at the Ac and fAc termini; sequences at which the Ac and fAc termini were formerly inserted are joined together at the site marked by the X. (C) The excised transposon ends reinsert at a site between a and b. The DNA between fAc and the insertion site is inverted.