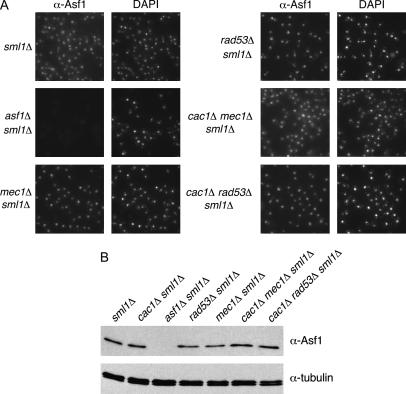
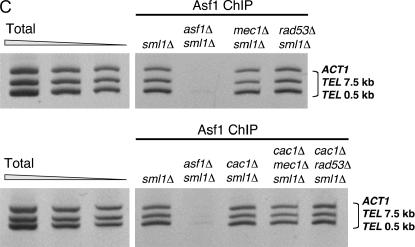
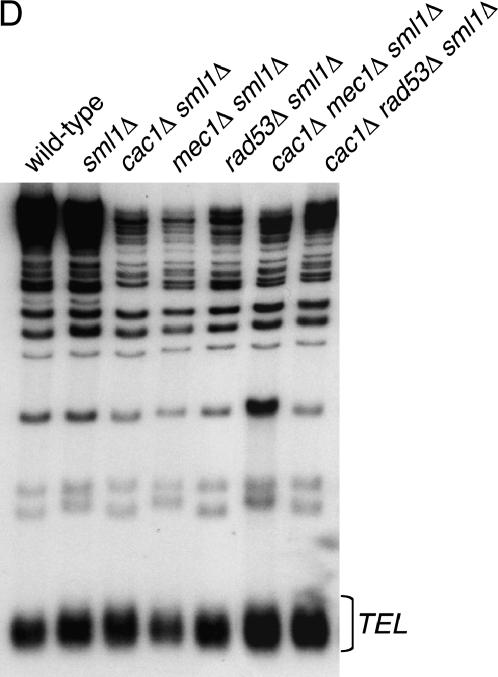
Figure 5.
Ablation of MEC1 or RAD53 gene function does not interfere with Asf1 nuclear localization, expression, or chromatin association and does not cause gross changes in average telomere length. (A) Asf1 immunofluorescence. Strains of the indicated genotypes were spheroplasted briefly and incubated with a rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against the conserved core of Asf1 (Daganzo et al. 2003). A Cy3-conjugated anti-rabbit antibody was used for secondary detection. Cells were incubated with DAPI to detect nuclear staining. (B) Immunoblot analysis of Asf1 protein levels. Crude cell extracts prepared from strains of the indicated genotypes were normalized for total protein and resolved on a 10% SDS-PAGE gel. After transfer of proteins to nitrocellulose membrane, the blot was probed with rabbit anti-Asf1 and rat anti-tubulin. (C) Chromatin immunoprecipitation of Asf1. Crosslinked chromatin was immunoprecipitated with rabbit anti-Asf1 sera. PCR analysis of ChIP eluates was performed with oligonucleotides specific for ACT1, 0.5 kb from telomere VI-R and 7.5 kb from telomere VI-R. Total chromatin was titrated to determine the linear range of the PCR; the 1:64, 1:128, and 1:256 dilutions that fall within this range are shown. For immunoprecipitations, one-fiftieth of the eluates were used for PCR analysis. (D) DNA blot analysis of telomere length. Average telomere length is indicated by the bracket. Strains in A–D were: wild type (PKY090), sml1Δ (PKY2503), cac1Δ sml1Δ (PKY1769), asf1Δ sml1Δ (PKY3045), mec1Δ sml1Δ (PKY2719), rad53Δ sml1Δ (PKY2702), cac1Δ mec1Δ sml1Δ (PKY2723), and cac1Δ rad53Δ (PKY2711).