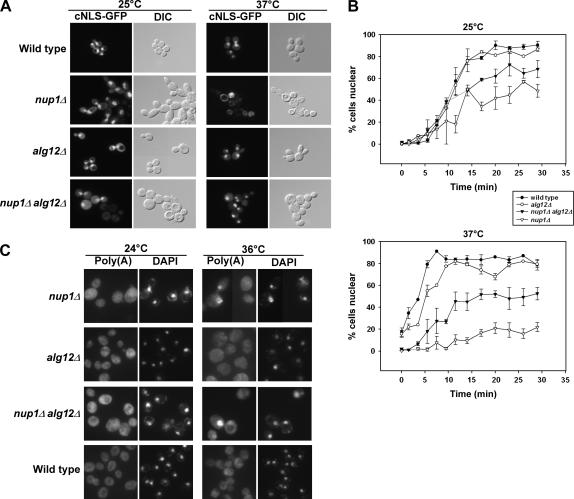
Figure 3.
Deletion of ALG12 suppresses nup1Δ protein import defects but not poly(A)+ RNA export defects. (A) Wild-type (KBY675), nup1Δ (KBY669), alg12Δ (KBY673), and nup1Δ alg12Δ (KBY671) cells expressing a cNLS fused to GFP (Shulga et al. 1996) were grown to early log phase at 25° and then retained at 25° or shifted to 37° for 3 hr. Cells were observed by direct fluorescence (cNLS-GFP) or differential interference contrast microscopy. (B) Wild-type (KBY675), nup1Δ (KBY669), alg12Δ (KBY673), and nup1Δ alg12Δ (KBY671) cells were examined for cNLS-GFP import kinetics (Shulga et al. 1996; see materials and methods). Briefly, cells expressing cNLS-GFP were treated with 2-deoxyglucose and sodium azide for 1 hr, washed, and then assayed for cNLS reimport by fluorescence microscopy. Import rate was determined by plotting the percentage of cells exhibiting nuclear fluorescence of cNLS-GFP vs. time. (Top) Relative cNLS-GFP import rates in cells grown at 25°. (Bottom) Cultures shifted to 37° for 3 hr and retained in 37° media throughout the import assay. Data represent mean values from at least three independent experiments. Error bars represent standard error of the mean. (C) Wild-type, nup1Δ, alg12Δ, and nup1Δ alg12Δ cells were grown to early log phase at 24° and then incubated at 24° or shifted to 36° for 3 hr. Cells were fixed, permeabilized, and incubated with a digoxigenin-conjugated oligo(dT)50 probe. Hybridized probe was detected using FITC-associated antidigoxigenin antibodies (Amberg et al. 1992). “Poly(A)” represents localization of polyadenylated RNA, as detected by the oligo(dT) probe. “DAPI” indicates the location of DAPI-stained nuclei in the same cells.