Figure 2.
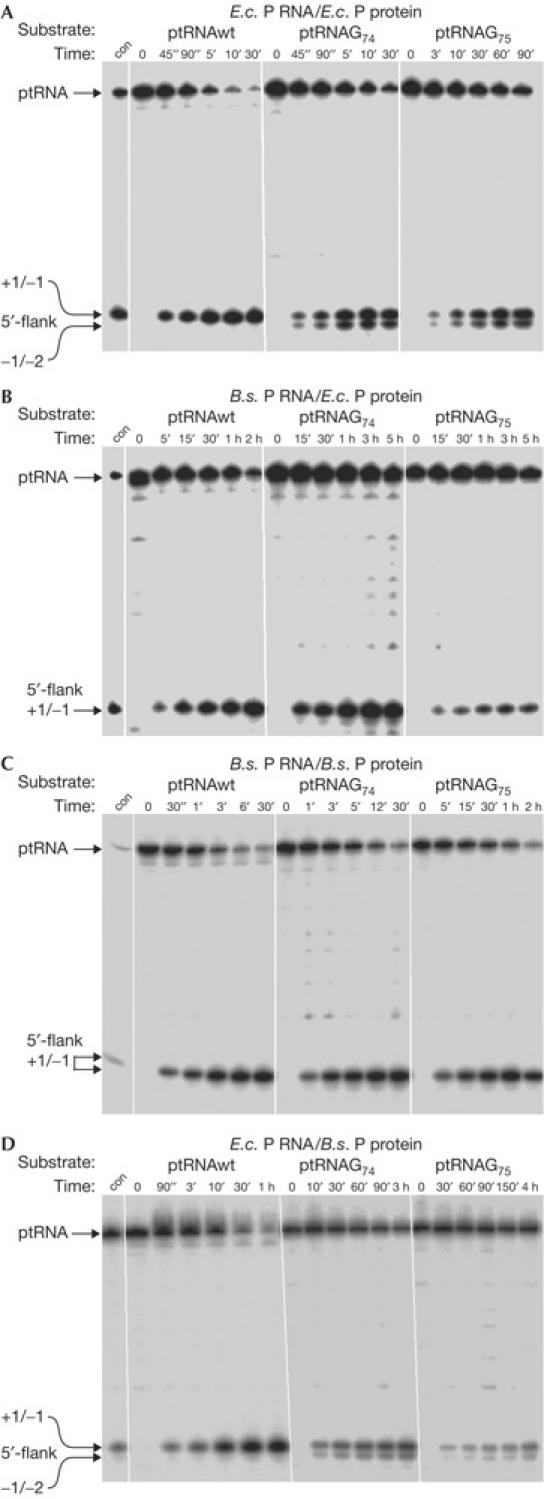
Processing and cleavage site selection of hybrid ribonuclease P (RNase P) holoenzymes isolated from Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis complementation strains. (A,B) RNase P partially purified from E. coli DW2 or (C,D) B. subtilis SSB318; holoenzymes contained E. coli P RNA in (A,D) or B. subtilis P RNA in (B,C). con, control cleavage by E. coli RNase P RNA. For details, see Methods. 5′-Cleavage products are indicated on the left (canonical cleavage site at +1/−1, miscleavage at −1/−2). Although the amount of extract added to processing assays was equalized in (A–D), based on absorption at 260 nm, holoenzyme concentrations are probably identical only within one panel; E.c., E. coli; B.s., B. subtilis.
