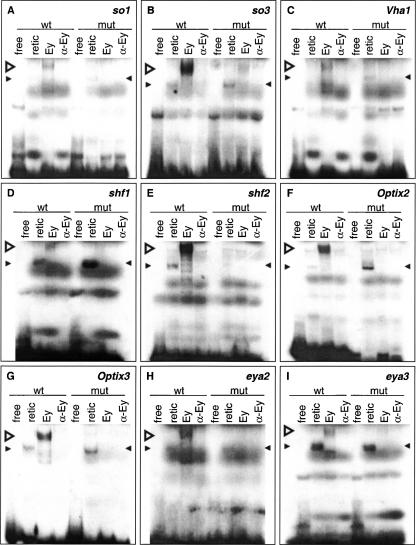
Figure 5.
Electromobility shift assays with reticulocyte-expressed Ey protein on 30-bp double-stranded oligonucleotides containing predicted wild-type or mutated Ey binding sites. Sites are from so (A,B), VhaPPA1–1 (C), shf (D,E), Optix (F,G), and eya (H,I). Both wild-type and mutated oligonucleotides were tested for binding to Ey. Four experiments were conducted with each probe with the first two lanes as negative controls. In vitro synthesized Ey was incubated with the probe as shown in the third lane. The binding is Ey specific since addition of polyclonal anti-Eyeless serum abolished the binding as shown in the fourth lane. Wild-type oligonucleotides were bound by Ey protein while mutated binding sites were not. (wt) Wild-type oligonucleotide, (mut) mutated oligonucleotide, (free) free probe alone, (retic) reticulocyte lysate with no plasmid, (Ey) reticulocyte-expressed Ey protein, (α-Ey) Ey protein with polyclonal anti-Eyeless serum added. Open arrowhead indicates specific gel shift; filled arrowheads indicate nonspecific binding.