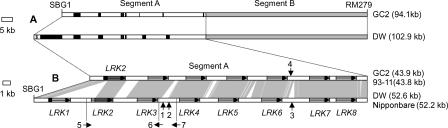
Figure 2.
Identification of the LRK gene cluster associated with the mapped QTL. (A) Schematic diagram of the sequence comparison in the QTL region flanked by the markers SBG1 and RM279 between Guichao2 (GC2) and Dongxiang wild rice (DW). Based on the extent of sequence divergence, the orthologous segment was divided into two sections. Segment B (represented by the lightly shaded rectangles) showed 99% sequence identity. The sequence of segment A exhibited extensive variation (represented by black bars or lines). (B) Sequence alignment of the LRK gene cluster in segment A between Guichao2 (or 93–11) and Dongxiang wild rice (or Nipponbare). Conserved sequences are connected by vertical areas. Horizontal arrows in shaded rectangles indicate polarity and position of LRK gene copies. Upward vertical arrows 1, 2, and 3 indicate position 337, 36, and 66-bp indels between Dongxiang wild rice and Nipponbare, respectively; downward vertical arrow 4 indicates the position of a 38-bp indel between Guichao2 and 93–11; horizontal arrows 5, 6, and 7 indicate polarity and the position of three gene fragments within the LRK cluster.