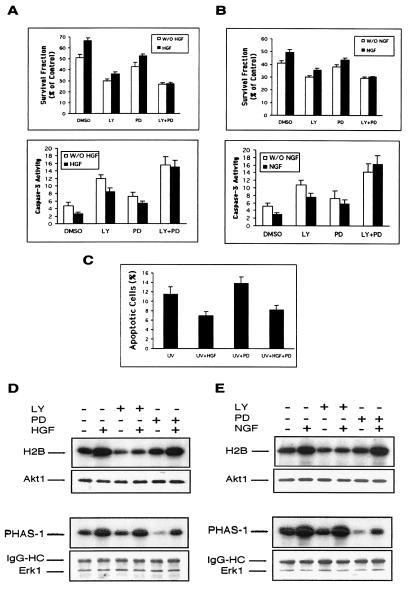
Figure 4.
Effect of LY294002 and PD098059 treatment on apoptosis and signaling of NIH 3T3 cells transfected with WT-Met or Trk-Met. (A and B) Both PI3-kinase/Akt and MAPK activities protect cells from apoptosis. After serum starvation and UV irradiation, WT-Met cells in A were incubated in the absence (−) or presence (+) of HGF (10 units/ml) plus LY294002 (20 μM) or PD058059 (30 μM) as indicated for 24 h. Trk-Met cells in B were treated in the same way as WT-Met cells, except that HGF was replaced with NGF (20 μg/ml). Cell survival in both cell lines was assessed by the MTT assay and caspase-3 activity assay. In the MTT assay, bars = mean ± SD of eight replicate wells; the experiment was conducted three times with similar results. In the caspase-3 activity assay, bars = mean ± SD of three independent experiments. (C) Apoptosis in NIH 3T3 cells transfected with WT-Met. Percentage of apoptotic cells was determined by Hoechst 33342 staining as described in Fig. 2. (D and E) PI3-kinase/Akt and MAPK signaling by HGF/Met. NIH 3T3 cells transfected with WT-Met in D were incubated in serum-free medium for 16 h and stimulated with or without HGF (10 units/ml) for 10 min. LY294002 (20 μM) or PD098059 (30 μM) was added 30 min before stimulation. Trk-Met cells in E were treated in the same way as WT-Met cells, except that HGF was replaced with NGF (20 μg/ml). Lysates were immunoprecipitated with antibodies to Akt1 or ERK1 and assayed for kinase activity. (D and E Upper) Histone 2B or PHAS-1 phosphorylation by Akt1 or MAPK activity, respectively. (D and E Lower) Western blot analysis of immunoprecipitates by using rabbit polyclonal anti-Akt1 or anti-ERK1 antibodies, demonstrating equivalent loading in each lane.