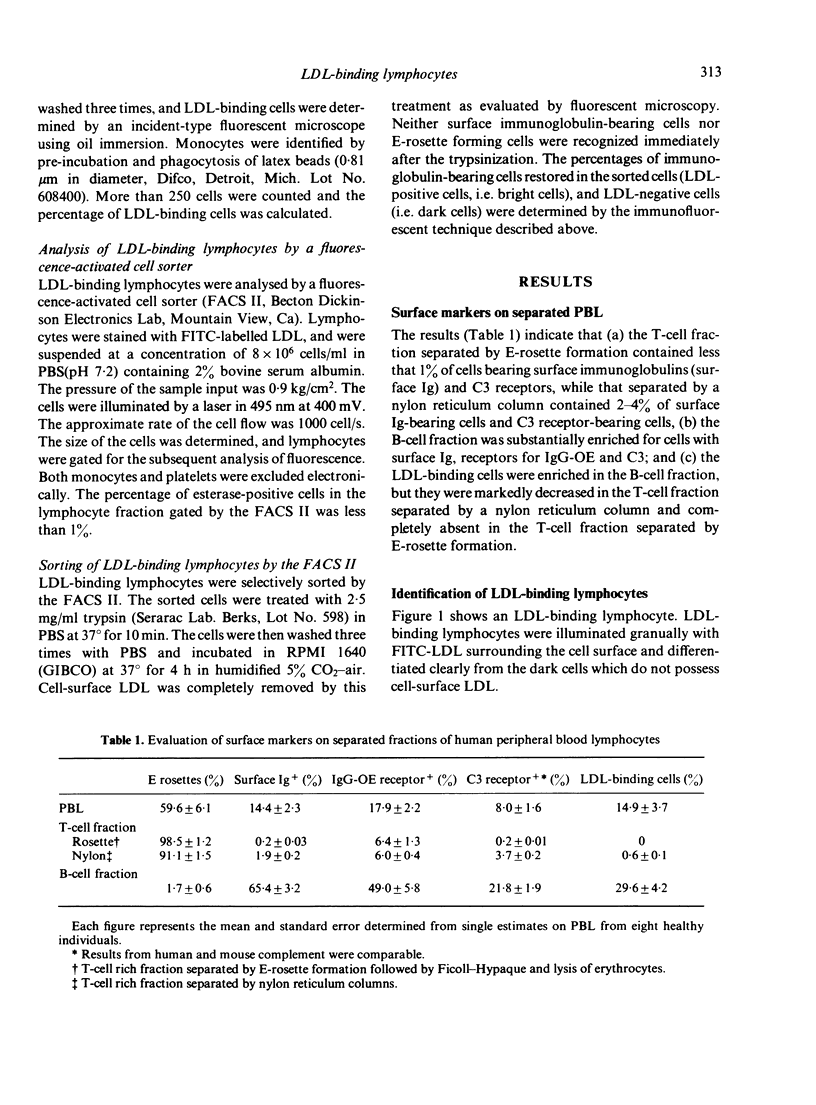
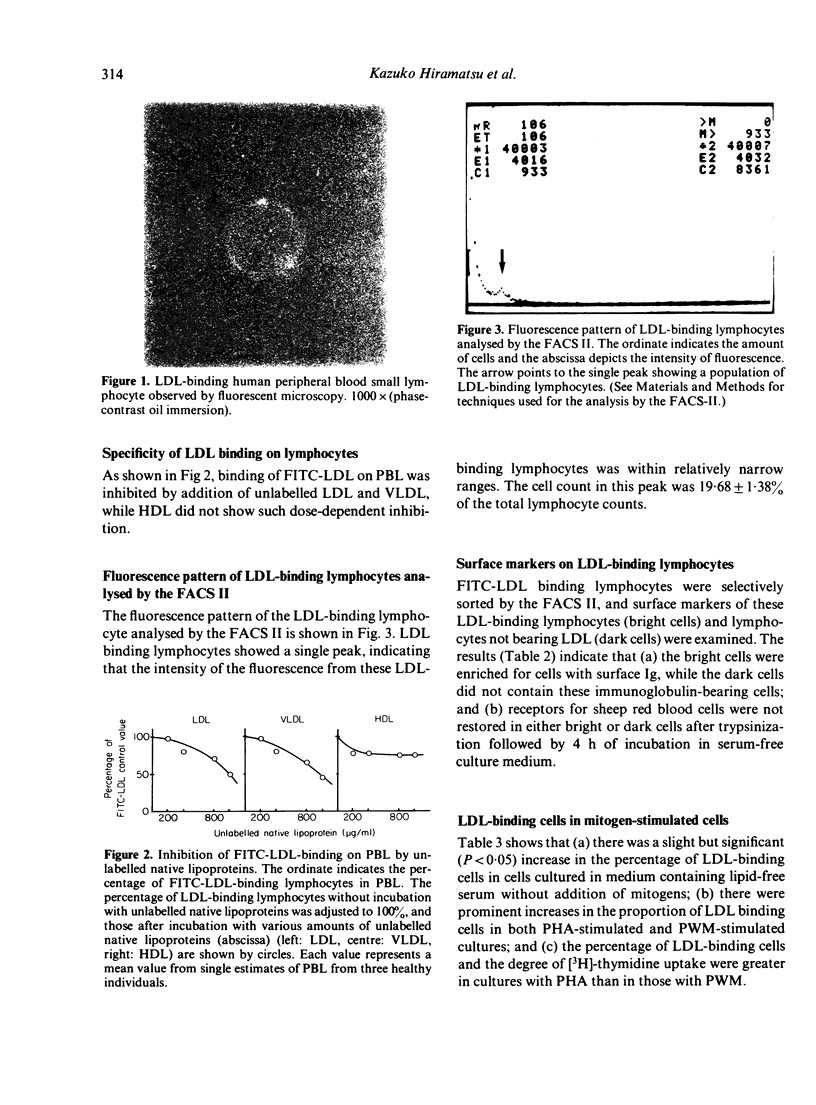
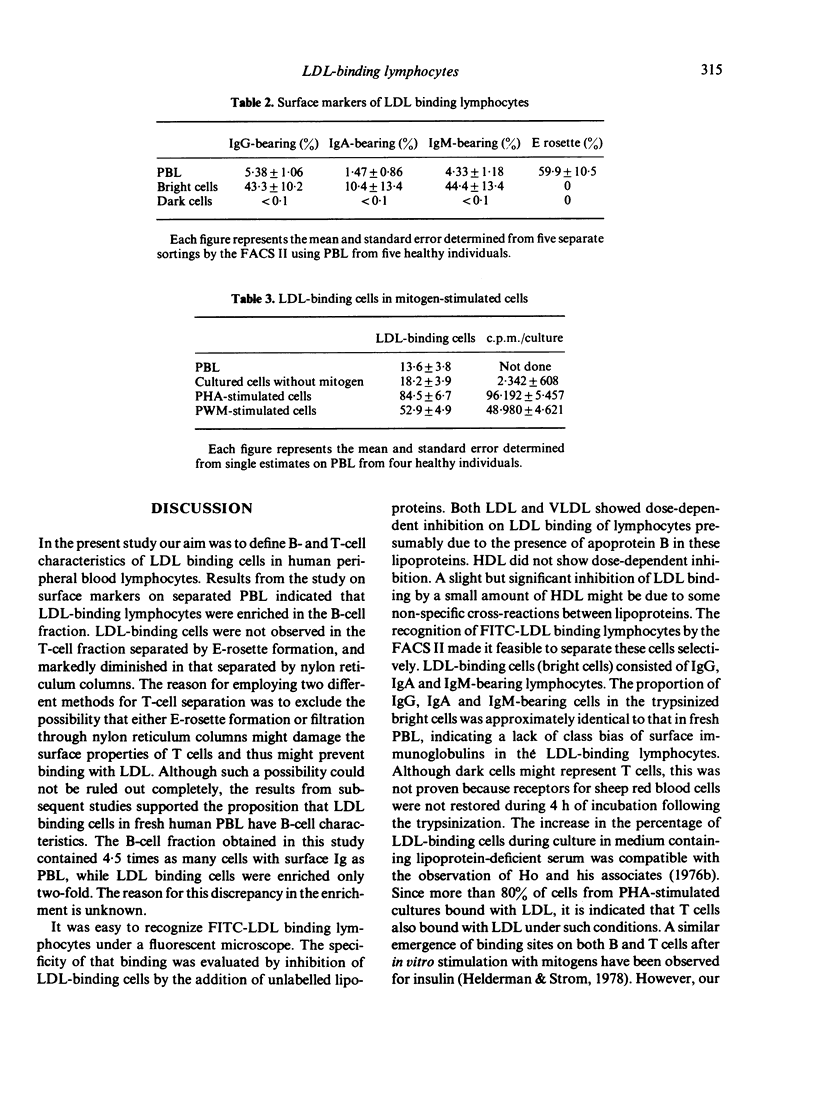
Abstract
Surface properties of low density lipoprotein (LDL)-binding lymphocytes were evaluated to determine whether LDL binds with a subpopulation of human peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL). B- and T-cell rich fractions were prepared from PBL using E-rosette formation or nylon reticulum columns. Binding of FITC-labelled LDL with these cell fractions was determined with a fluorescent microscope and a fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS II). The specificity of the binding was evaluated by a dose-dependent inhibition of LDL binding with the addition of unlabelled lipoproteins. In parallel studies, surface properties including E-rosette formation, surface immunoglobulins, and receptors for IgG-Fc, as well as human and mouse C3 were examined. LDL binding lymphocytes were enriched in the B-cell rich fraction, and depleted in the T-cell rich fraction. In addition, FITC-LDL binding lymphocytes were selectively collected by the FACS II. These LDL binding cells restored surface immunoglobulins after incubation in serum-free medium following trypsinization. The majority of lymphocytes stimulated by PHA and PWM in vitro bound with LDL. It is concluded that LDL binds with B cells in fresh human PBL, while it binds with B and T cells in mitogen-stimulated lymphocytes. It is suggested that the selective collection of LDL binding lymphocytes by the FACS II can be applied to the evaluation of cellular interaction of these cells in various immunological reactions.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyle W. An extension of the 51Cr-release assay for the estimation of mouse cytotoxins. Transplantation. 1968 Sep;6(6):761–764. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196809000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss L. K., Edgington T. S. Differential sensitivity of lymphocyte subpopulations to suppression by low density lipoprotein inhibitor, an immunoregulatory human serum low density lipoprotein. J Clin Invest. 1979 Feb;63(2):193–201. doi: 10.1172/JCI109289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels J. C., Sakai H., Cobb E. K., Remmers A. R., Jr, Sarles H. E., Fish J. C., Levin W. C., Ritzmann S. E. Altered nucleic acid synthesis patterns in lymphocytes from patients with chronic uremia. Am J Med Sci. 1970 Mar;259(3):214–227. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197003000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagmann J., Weiler I., Waelti E. Effects of low density lipoproteins on lymphocyte stimulation. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jan 15;97(2):230–232. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho Y. K., Brown M. S., Kayden H. J., Goldstein J. L. Binding, internalization, and hydrolysis of low density lipoprotein in long-term lymphoid cell lines from a normal subject and a patient with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. J Exp Med. 1976 Aug 1;144(2):444–455. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.2.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho Y. K., Brown S., Bilheimer D. W., Goldstein J. L. Regulation of low density lipoprotein receptor activity in freshly isolated human lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1976 Dec;58(6):1465–1474. doi: 10.1172/JCI108603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho Y. K., Smith R. G., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor activity in human acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Blood. 1978 Dec;52(6):1099–1114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]