Abstract
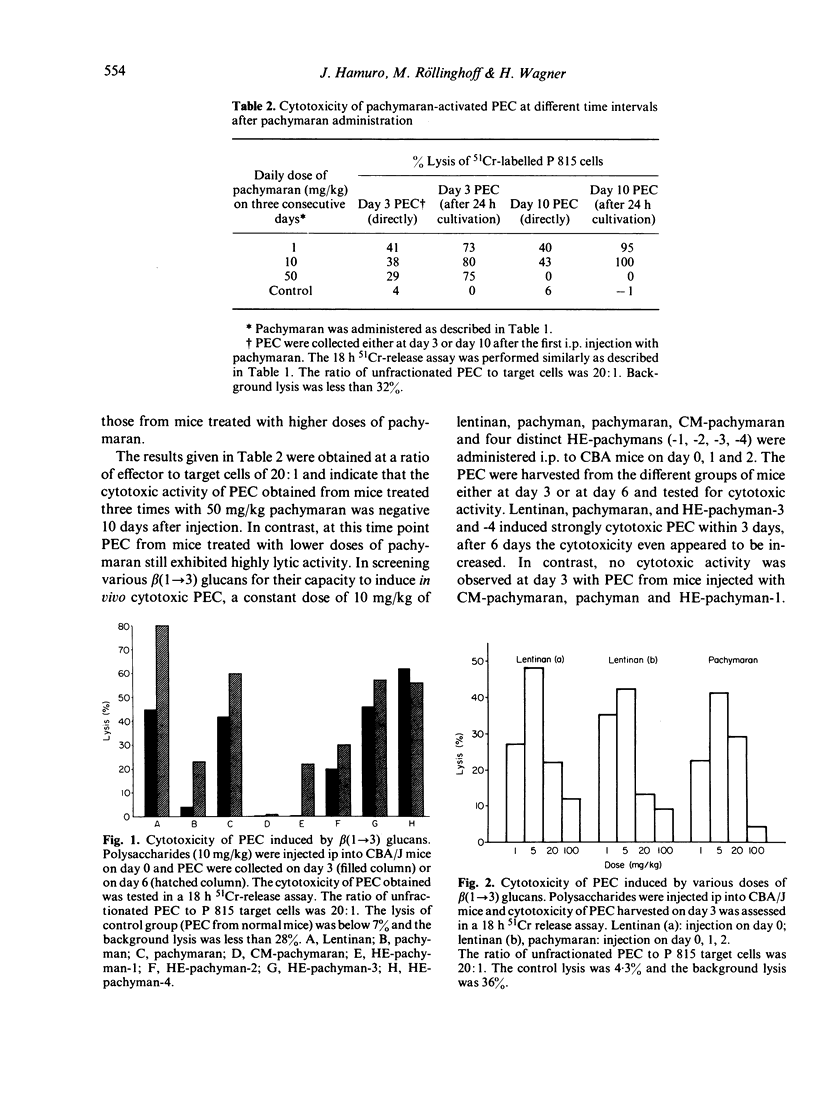
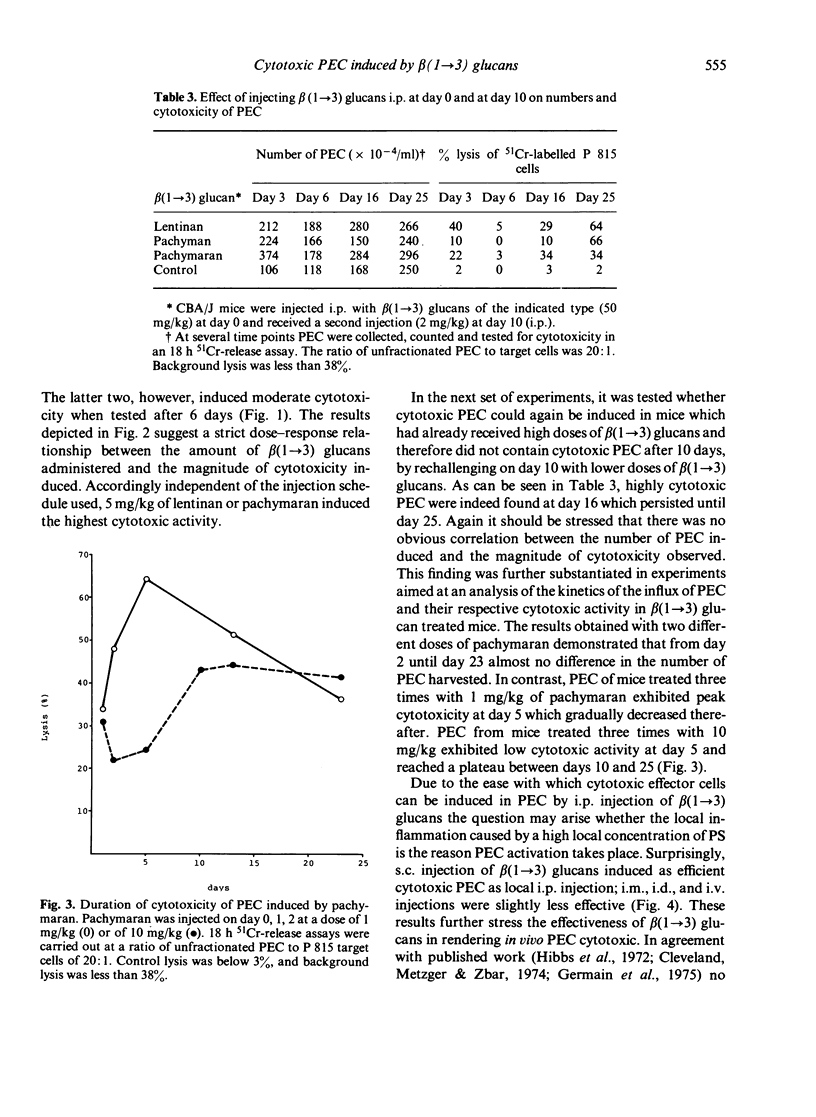
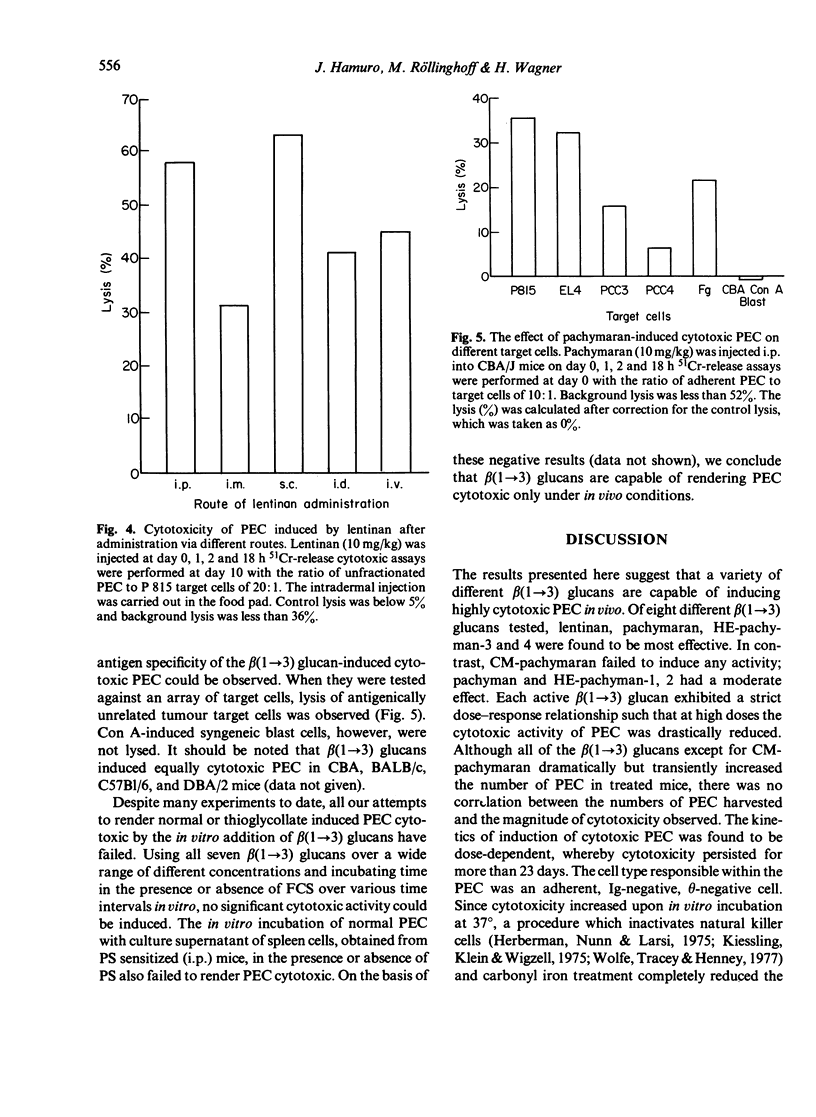
Eight distinct polysaccharides (PS) of beta(1 leads to 3) glucan type were tested for their capacity to render murine peritoneal exudate cells (PEC) cytotoxic. After intraperitoneal injection of lentinan, pachymaran and HE-pachyman 3 and 4 highly cytotoxic PEC were induced. Pachyman and HE-pachyman 1 and 2 were of moderate effect, whereas CM-pachymaran and HE-pachyman 3 and 4, highly cytotoxic PEC were induced. Pachyman and HE-pachymacrophages. The induction of PEC-dependent cytotoxicity exhibited a strict dose relationship. Optimal administration of PS resulted in the induction of cytotoxicity, which persisted for more than 25 days. Surprisingly, none of the PS tested was capable of rendering normal or thioglycollate-induced PEC cytoxic under in vitro conditions. It is suggested that the capacity of PS to render in vivo macrophages cytotoxic is related to the potency of these PS to activate the alternative pathway of complement system (APC) in so far as C3b may be the essential component required to render macrophages cytotoxic.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BIOZZI G., STIFFEL C., HALPERN B. N., MOUTON D. [Effect of inoculation with Calmette-Guerin bacillus on the development of Ehrlich ascites tumor in the mouse]. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1959;153:987–989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruley-Rosset M., Florentin I., Khalil A. M., Mathé G. Nonspecific macrophage activation by systemic adjuvants. Evaluation by lysosomal enzyme and in vitro tumoricidal activities. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1976;51(5):594–607. doi: 10.1159/000231638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro J. E. Antitumour effects of Corynebacterium parvum in mice. Eur J Cancer. 1974 Feb;10(2):121–127. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(74)90063-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chihara G., Hamuro J., Maeda Y., Arai Y., Fukuoka F. Antitumor polysaccharide derived chemically from natural glucan (pachyman). Nature. 1970 Mar 7;225(5236):943–944. doi: 10.1038/225943a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chihara G., Hamuro J., Maeda Y., Arai Y., Fukuoka F. Fractionation and purification of the polysaccharides with marked antitumor activity, especially lentinan, from Lentinus edodes (Berk.) Sing. (an edible mushroom). Cancer Res. 1970 Nov;30(11):2776–2781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chihara G., Maeda Y., Hamuro J., Sasaki T., Fukuoka F. Inhibition of mouse sarcoma 180 by polysaccharides from Lentinus edodes (Berk.) sing. Nature. 1969 May 17;222(5194):687–688. doi: 10.1038/222687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie G. H., Bomford R. Mechanisms of macrophage activation by Corynebacterium parvum. I. In vitro experiments. Cell Immunol. 1975 May;17(1):141–149. doi: 10.1016/s0008-8749(75)80014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland R. P., Meltzer M. S., Zbar B. Tumor cytotoxicity in vitro by macrophages from mice infected with mycobacterium bovis strain BCG. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Jun;52(6):1887–1895. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.6.1887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennert G., Tucker D. Antitumor polysaccharide lentinan. A T cell adjuvant. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Nov;51(5):1727–1729. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.5.1727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dresser D. W., Phillips J. M. The orientation of the adjuvant activities of Salmonella typhosa lipopolysaccharide and lentinan. Immunology. 1974 Nov;27(5):895–902. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R., Grant C. K., Cox H., Steele K., Alexander P. Thymus-derived lymphocytes produce an immunologically specific macrophage-arming factor. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1318–1322. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern B. N., Biozzi G., Stiffel C., Mouton D. Inhibition of tumour growth by administration of killed corynebacterium parvum. Nature. 1966 Nov 19;212(5064):853–854. doi: 10.1038/212853a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamuro J., Röllinghoff M., Wagner H. beta(1 leads to 3) Glucan-mediated augmentation of alloreactive murine cytotoxic T-lymphocytes in vivo. Cancer Res. 1978 Sep;38(9):3080–3085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamuro J., Wagner H., Röllinghoff M. Beta (1-3) glucans as a probe for T cell specific immune adjuvants. II. Enhanced in vitro generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1978 Jul;38(2):328–335. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90064-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamuro J., Yamashita Y., Ohsaka Y., Maeda Y. Y., Chihara G. Carboxymethylpachymaran, a new water soluble polysaccharide with marked antitumour activity. Nature. 1971 Oct 15;233(5320):486–488. doi: 10.1038/233486a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Nunn M. E., Lavrin D. H. Natural cytotoxic reactivity of mouse lymphoid cells against syngeneic acid allogeneic tumors. I. Distribution of reactivity and specificity. Int J Cancer. 1975 Aug 15;16(2):216–229. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910160204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Lambert L. H., Jr, Remington J. S. In vitro nonimmunologic destruction of cells with abnormal growth characteristics by adjuvant activated macrophages. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Mar;139(3):1049–1052. doi: 10.3181/00379727-139-36295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. M., Morahan P. S., Regelson W. Induction of macrophage-mediated tumor-cell cytotoxicity by pyran copolymer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Jun;52(6):1919–1923. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.6.1919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R. Cytostatic elimination of syngeneic rat tumor cells in vitro by nonspecifically activated macrophages. J Exp Med. 1973 Sep 1;138(3):625–644. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.3.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling R., Klein E., Wigzell H. "Natural" killer cells in the mouse. I. Cytotoxic cells with specificity for mouse Moloney leukemia cells. Specificity and distribution according to genotype. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Feb;5(2):112–117. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda Y. Y., Chihara G. Periodical consideration on the establishment of antitumor action in host and activation of peritoneal exudate cells by lentinan. Gan. 1973 Aug;64(4):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Hill V. M., Terry W. D. Isolation of a subpopulation of adherent peritoneal cells with anti-tumour activity. Nature. 1976 Mar 11;260(5547):146–148. doi: 10.1038/260146a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J., Kirstein D. P. T-cell-mediated concomitant immunity to syngeneic tumors. I. Activated macrophages as the expressors of nonspecific immunity to unrelated tumors and bacterial parasites. J Exp Med. 1977 Feb 1;145(2):275–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLD L. J., CLARKE D. A., BENACERRAF B. Effect of Bacillus Calmette-Guerin infection on transplanted tumours in the mouse. Nature. 1959 Jul 25;184(Suppl 5):291–292. doi: 10.1038/184291a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfizenmaier K., Trostmann H., Röllinghoff M., Wagner H. Cell-mediated allograft responses in vitro. VI. Studies on macrophage-mediated cytotoxicity. Immunology. 1975 Dec;29(6):967–976. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piessens W. F., Churchill W. H., Jr, David Macrophages activated in vitro with lymphocyte mediators kill neoplastic but not normal cells. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):293–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schorlemmer H. U., Bitter-Suermann D., Allison A. C. Complement activation by the alternative pathway and macrophage enzyme secretion in the pathogenesis of chronic inflammation. Immunology. 1977 Jun;32(6):929–940. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz R. M., Chirigos M. A., Heine U. I. Functional and morphologic characteristics of interferon-treated macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1978 Jan;35(1):84–91. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90128-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner H., Götze D., Ptschelinzew L., Röllinghoff M. Induction of cytotoxic T lymphocytes against I-region-coded determinants: in vitro evidence for a third histocompatibility locus in the mouse. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1477–1487. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner H., Starzinski-Powitz A., Röllinghoff M., Golstein P., Jakob H. T-cell-mediated cytotoxic immune responses to F9 teratocarcinoma cells: cytolytic effector T cells lyse H-2-negative F9 cells and syngeneic spermatogonia. J Exp Med. 1978 Jan 1;147(1):251–264. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.1.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe S. A., Tracey D. E., Henney C. S. BCG-induced murine effector cells. II. Characterization of natural killer cells in peritoneal exudates. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1152–1158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


