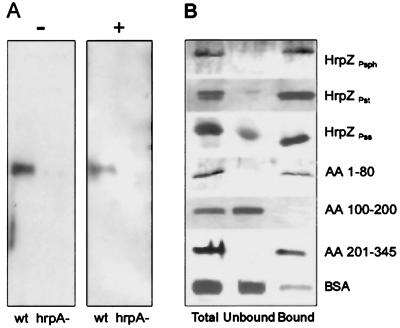
Figure 3.
HrpZPsph interacts with lipid membranes. (A) Psph race-6 wild-type (wt) and race-6 mutant hrpA− were grown in hrp-inducing minimal media (8) in the absence (−) or presence (+) of liposomes. Proteins prepared from the supernatant or proteoliposomes were separated and analyzed by SDS/PAGE immunoblotting with an anti-HrpZPsph antiserum. (B) TRANSIL beads coated with 1-hexadecanoyl-2-(cis-9-octadecenoyl)-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (POPC)/1-hexadecanoyl-2-(cis-9-octadecenoyl)-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (POPE) (80:20) were incubated for 1 h with 1 μM of the proteins indicated (Total). After separation of lipid-bound (Bound) from unbound material, proteins were analyzed by SDS/PAGE and silver staining. HrpZPst, HrpZ from P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000; HrpZPss, HrpZ from P. syringae pv. syringae; AA 1–80, AA 100–200, AA 201–345, HrpZPsph fragment encompassing the N-terminal 80 amino acid (AA) residues, amino acids 100–200, or the C-terminal amino acids 201–345, respectively.