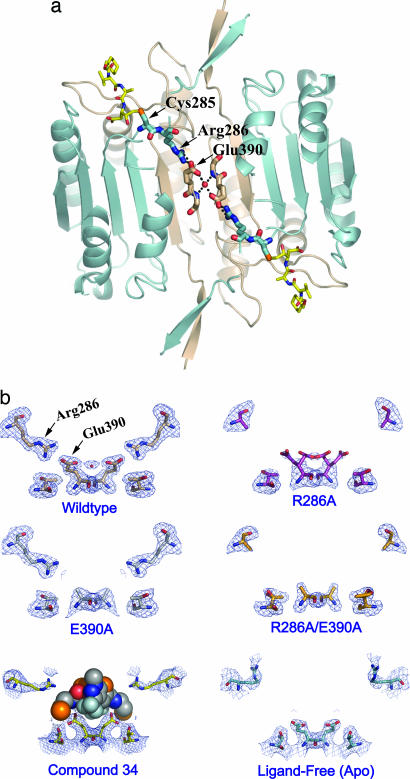
Fig. 3.
Structural analysis of mutations in the allosteric circuit of caspase-1. (a) A network of interactions across the dimer interface of caspase-1 in the z-VAD-FMK-inhibited protein. The inhibitor is shown as yellow sticks in the upper left and lower right. The active-site Cys-285 and Arg-286 are displayed as blue sticks, Glu-390 at the dimer interface as tan sticks, and a water molecule mediating the interaction between the two Glu residues is shown as a red sphere. (b) The x-ray crystal structure of each allosteric-circuit mutant was determined in the presence of the active-site inhibitor z-VAD-FMK. All structures (PDB ID codes 2FQS, R286A; 2FQU, E390A; and 2FQV, R286A/E390A) adopted a dimeric structure very similar to that of the wild-type enzyme in complex with an active-site inhibitor (PDB ID code 2FQR). No significant conformational changes were observed in the enzymes except for those involving residues in the allosteric circuit. The 2Fo − Fc electron density for residues Arg-286, Glu-390, and Thr-388 is displayed. (Bottom Left) The position of Compound 34 displayed as spheres. (Bottom Right) The ligand-free (apo) conformation of caspase-1.