Fig. 6.
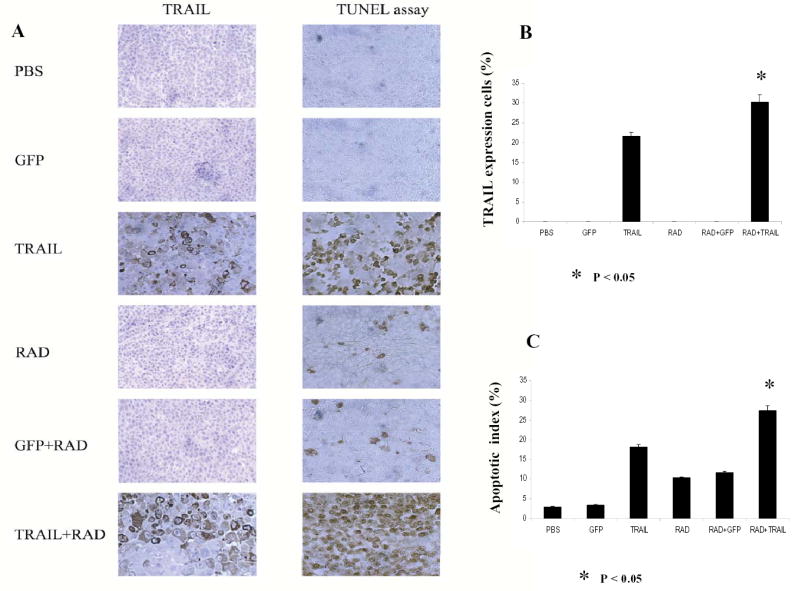
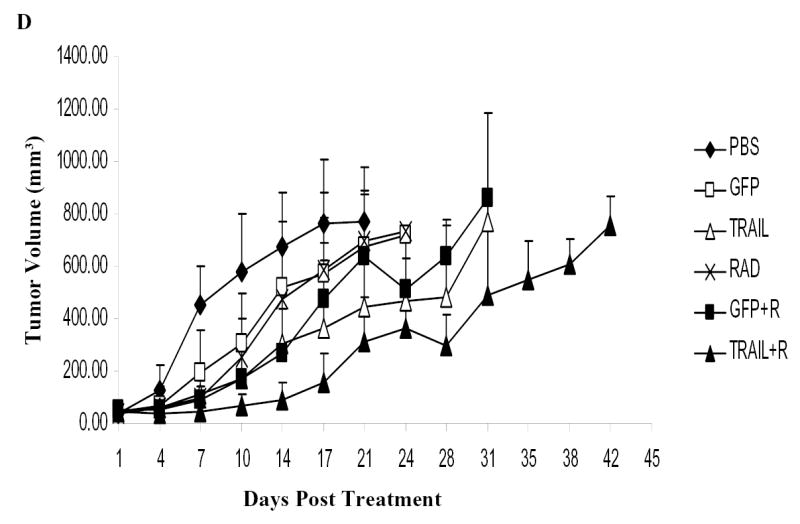
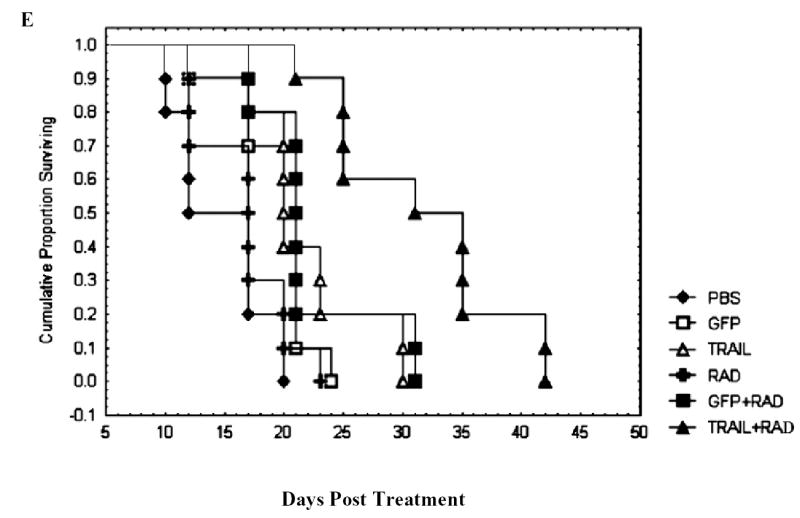
Ad/TRAIL-F/RGD (TRAIL) combined with radiotherapy enhanced apoptosis, inhibited tumor growth in vivo and prolonged mice survival. Seg-1 cells were grown as xenograft tumors in nude mice, and mice bearing tumors of 80 to 100 mm3 were treated with PBS, Ad/CMV-GFP alone (GFP), TRAIL alone, radiotherapy (RAD) alone, GFP +RAD, or TRAIL+RAD. Tumor volumes were then measured. A, Representative fields of TRAIL expression by immunohistochemistry (left panel) and tumor cell apoptosis by TUNEL assay (right panel) in Seg-1 tumors 3 days after receiving various treatments. B, The percentage of TRAIL-positive tumor cells as counted under a light microscope. C, Apoptotic index in the various treatment groups as determined by counting at least 1,000 cells per sample under a light microscope. The apoptosis index was calculated as a percentage of total number of cells scored. Bars, SE. D, Tumor growth delay curves. Data are presented as the mean ± standard error. ANOVA was performed using the SAS procedure and SAS software (version 6.12) to determine the statistical significance of the differences on tumor growth between each treatment group. P<0.05 in Figure 6B,C, D as comparison between Ad/TRAIL-F/RGD plus radiation and PBS, Ad/CMV-GFP, Ad/TRAIL-F/RGD, radiation, Ad/CMV-GFP plus radiation respectively and combined. E, Animals alive as a function of time after treatment. We used the Kaplan-Meier method for our survival analysis.
