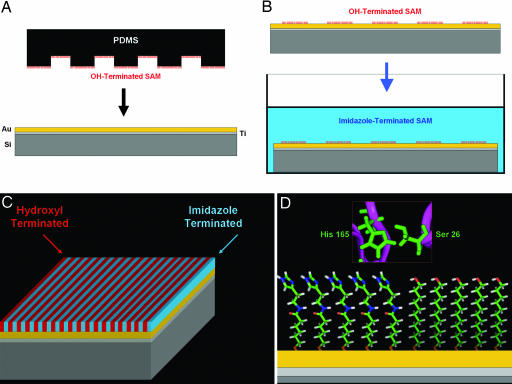
Fig. 5.
Schematic depicting the formation of a bifunctional SAM. (A) A poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) stamp inked with an alkane thiolate (e.g., OH-terminated) is brought into contact with a gold surface, facilitating transfer of the thiol to the gold through adsorption with sulfur (23). (B) After the initial printing of the first alkane thiol, the wafer is then immersed in a different alkane thiol (e.g., imidazole-terminated) solution to form the second monolayer resulting in a bifunctionalized SAM surface (C) that presents the essential functionalities necessary for hydrolysis (D), similar to those found in silicatein.