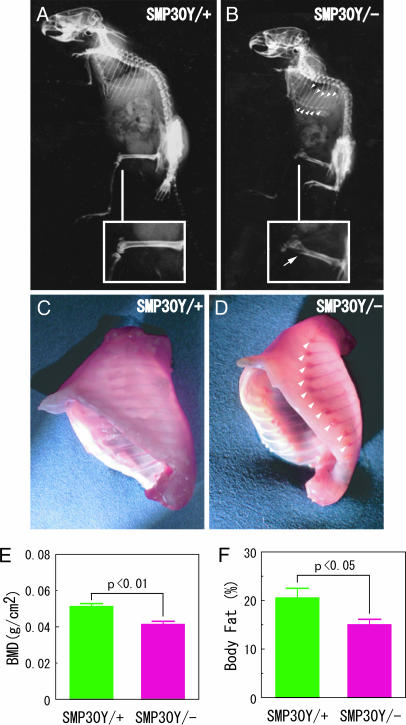
Fig. 5.
Osteogenic disorder of SMP30 knockout mice. SMP30Y− and SMP30Y+ mice at an age of 40 days were fed a vitamin C-deficient diet for 59 days (animals’ age was 99 days). (A–D) X-ray images show the skeletal structures of SMP30Y+ (A) and SMP30Y− (B) mice. Insets show enlargements of the femoral region; an arrow points to the distal femur fracture of a SMP30 knockout mouse. A rachitic rosary of the SMP30Y− mouse observed after evisceration (D) is compared with that area in a control mouse (C). Arrowheads in B and D indicate a rachitic rosary at the junction of costae and costal cartilage. (E and F) Subcranial total BMD (E) and body fat percentage (F) of SMP30Y− and SMP30Y+ mice were determined by PIXImus2 densitometry as described in Materials and Methods. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM of five or six animals.