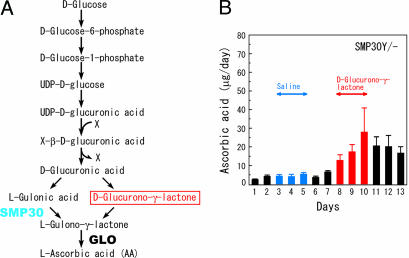
Fig. 6.
Increased excretion of AA in the urine after administration of d-glucurono-γ-lactone. (A) The pathway of AA biosynthesis. The pathway from d-glucose to l-gulonic acid is shared with that of early steps in the uronic acid cycle. X is a conjugating molecule for glucuronidation. GLO, l-gulono-γ-lactone oxidase. (B) SMP30Y− mice were fed autoclaved mouse chow for 60 days after weaning and were housed individually in metabolic cages starting on day 1. Saline was injected i.p. from day 3 to day 5; then, d-glucurono-γ-lactone (0.7 mg/g of body weight) dissolved in saline was injected i.p. from day 8 to day 10. Urine samples were collected, and their AA concentrations were measured. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM of four SMP30Y− mice.