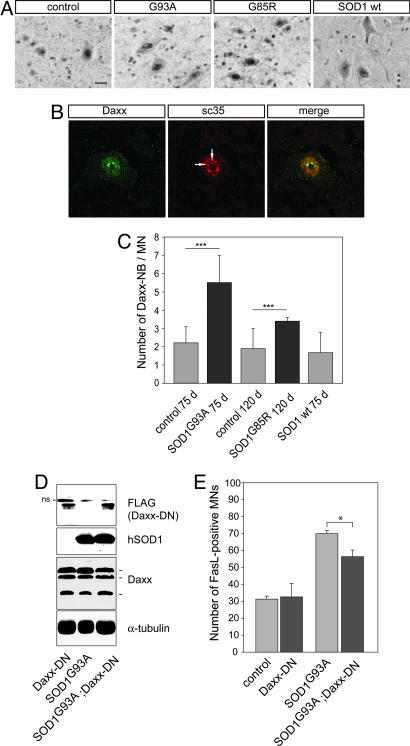
Fig. 5.
Daxx activation in lumbar motoneurons of mutant SOD1 mice and its functional relevance in the Fas/NO loop. (A) Immunolabeling reveals that Daxx accumulates in the nuclei of motoneurons and forms nuclear bodies. SOD1G93A,C57BL/6 littermates and SOD1WT mice were analyzed at age 75 days; SOD1G85R and C57BL/6 litter mice (C.R., data not shown) were analyzed at age 120 days. (Scale bar: 20 μm.) (B) Daxx nuclear bodies (arrows) are associated with a subpopulation of nuclear speckles, as detected by confocal analysis of Daxx- and sc35-immunostained SOD1G93A lumbar spinal cords at age 75 days. (C) The number of Daxx nuclear bodies (Daxx-NBs) in L4 motoneurons was higher in SOD1G93A and SOD1G85R mice than in C57BL/6 or SOD1WT mice of the same age. Values represent means ± SD from three mice per genotype; ∗∗∗, P < 0.001, Student's t test. (D and E) Analysis of double transgenic SOD1G93A;Daxx-DN mice. (D) Western blots of protein extracts from lumbar spinal cords show that the dominant negative form of Daxx (Daxx-DN) and the human SOD1G93A are expressed at similar levels in double transgenic mice and in the parental mice at age 75 days. Daxx-DN was revealed with an anti-FLAG antibody that also detects a nonspecific (ns) upper band. Daxx-DN expression did not modify expression of endogenous Daxx because the three known Daxx isoforms of 70, 97, and 110 kDa (43) were detected at similar levels in all genotypes. (E) Transgenic Daxx-DN expression significantly reduced the percentage of FasL-positive motor neurons in double transgenic mutant SOD1G93A;Daxx-DN mice as compared with values in age-matched 75-day-old SOD1G93A mice. Values are means ± SD, n = 3 per genotype; ∗∗∗, P < 0.001, one-way ANOVA followed by Newman–Keuls post hoc analysis.