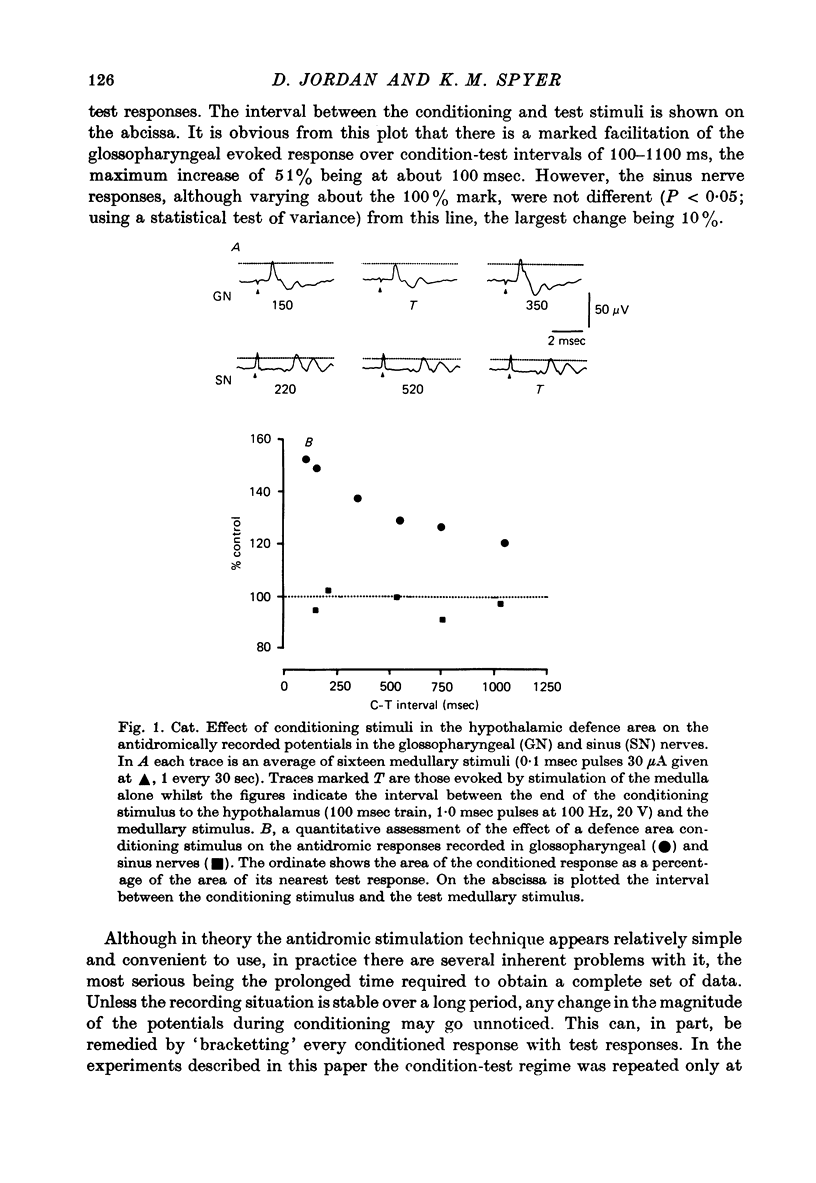
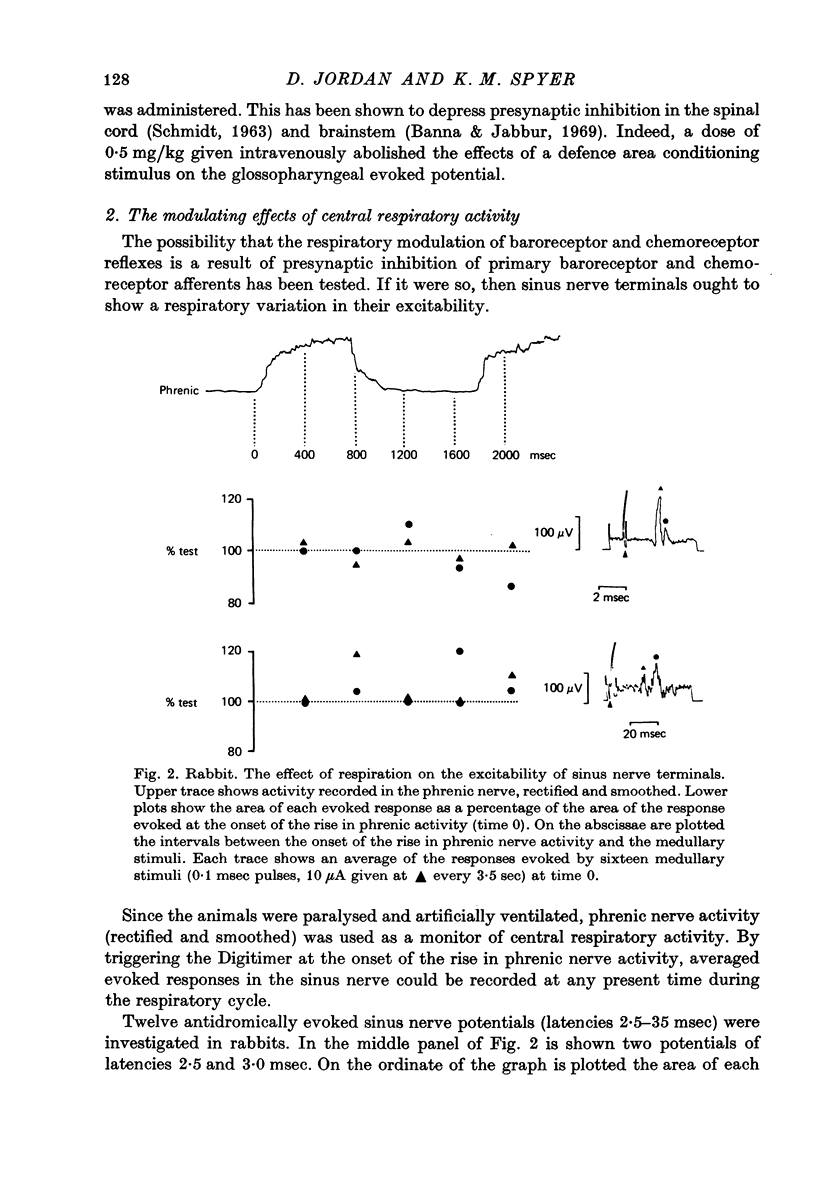
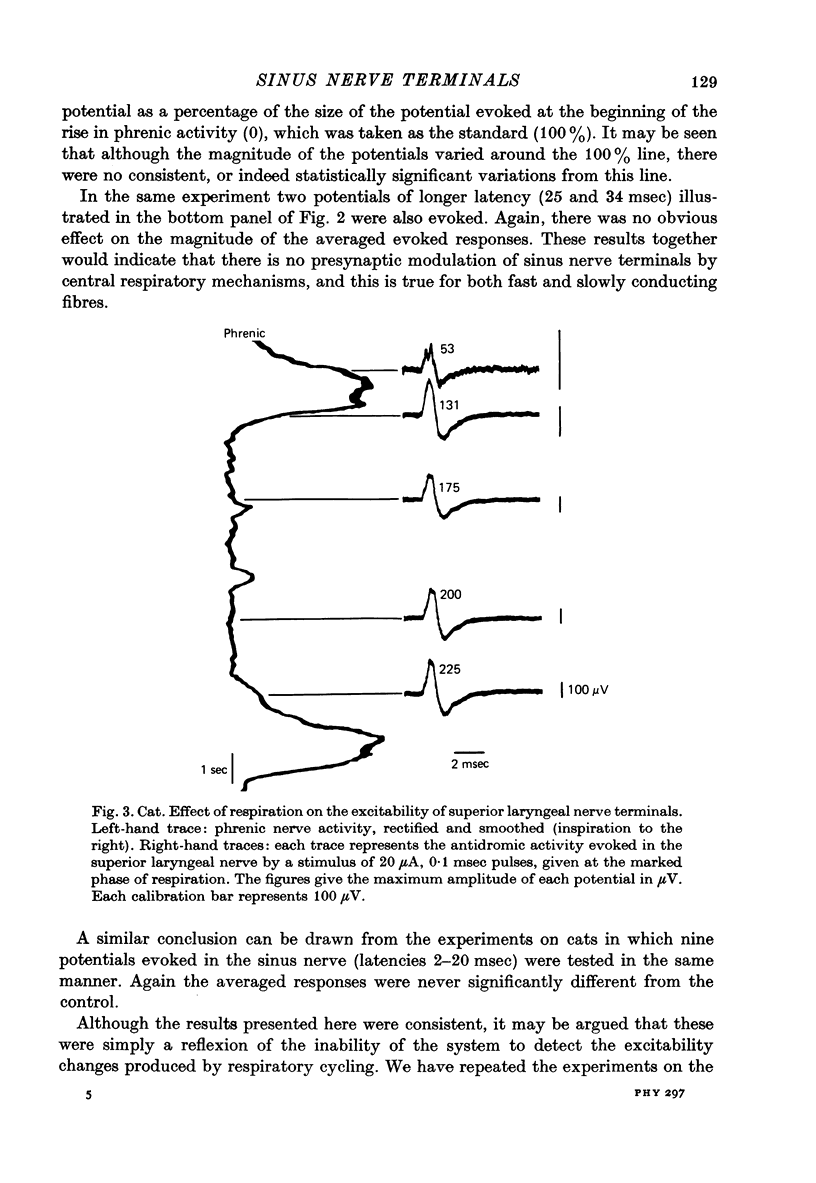
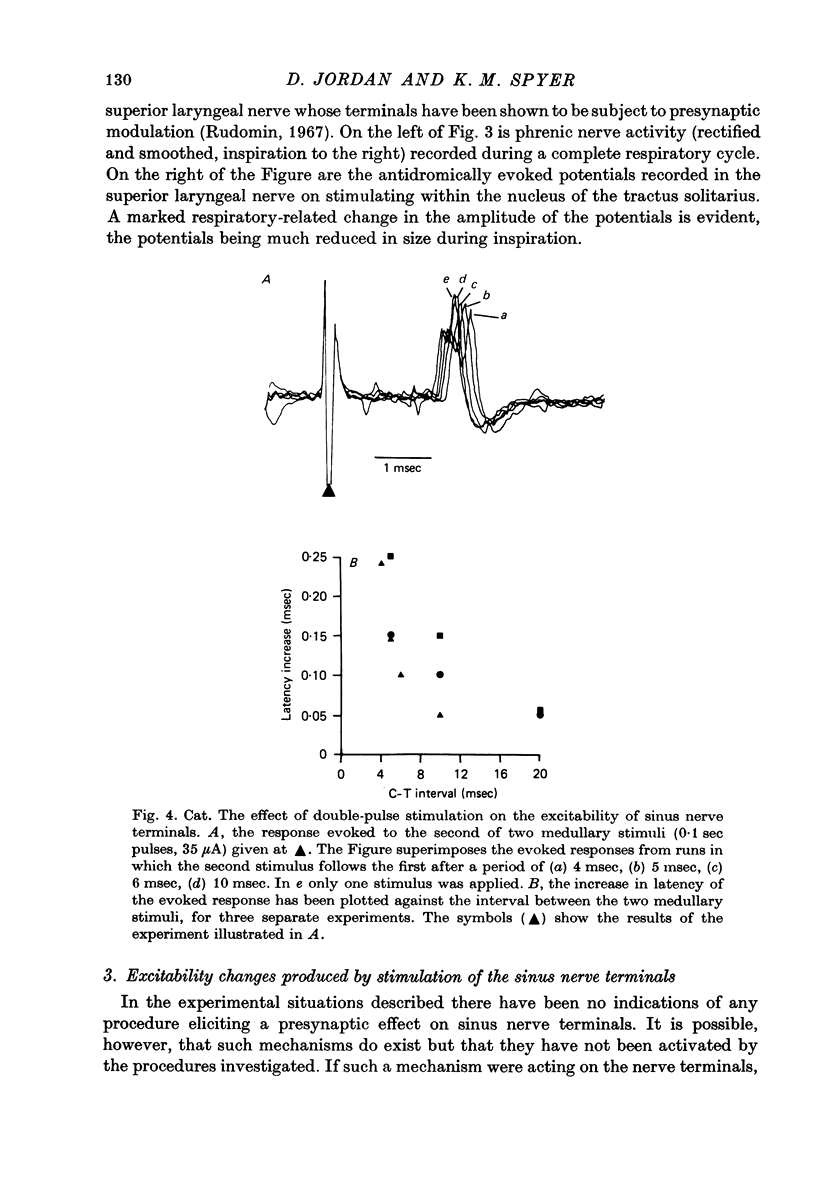
Abstract
1. The excitability of sinus nerve afferent terminals within the nucleus of the tractus solitarius has been studied in cats and rabbits using the technique of antidromic activation. 2. Conditioning stimuli to the hypothalamic defence area increased the excitability of some glossopharyngeal nerve afferents, though no such effects were observed on sinus nerve terminals. 3. Although the excitability of superior laryngeal nerve afferent terminals was observed to fluctuate in phase with the central respiratory cycle, no equivalent variation in sinus nerve terminal excitability were observed. 4. It is concluded that sinus nerve afferent terminals are not influenced by presynaptic mechanisms. Possible sites for the observed modulations of baroreceptor and chemoreceptor reflexes are discussed in the light of these results.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAHAMS V. C., HILTON S. M., ZBROZYNA A. Active muscle vasodilatation produced by stimulation of the brain stem: its significance in the defence reaction. J Physiol. 1960 Dec;154:491–513. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banna N. R., Jabbur S. J. Pharmacological studies on inhibition in the cuneate nucleus of the cat. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1969 May;8(3):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(69)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black A. M., Torrance R. W. Chemoreceptor effects in the respiratory cycle. J Physiol. 1967 Apr;189(2):59P–61P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba T., Doba N. Catecholaminergic axo-axonic synapses in the nucleus of the tractus solitarius (pars commissuralis) of the cat: possible relation to presynaptic regulation of baroreceptor reflexes. Brain Res. 1976 Feb 6;102(2):255–265. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90881-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba T., Doba N. The synaptic structure of catecholaminergic axon varicosities in the dorso-medial portion of the nucleus tractus solitarius of the cat: possible roles in the regulation of cardiovascular reflexes. Brain Res. 1975 Jan 24;84(1):31–46. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90798-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coote J. H., Hilton S. M., Perez-Gonzalez J. F. Inhibition of the baroreceptor reflex on stimulation in the brain stem defence centre. J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:549–560. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldridge F. L. The importance of timing on the respiratory effects of intermittent carotid body chemoreceptor stimulation. J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(2):319–333. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flock A., Russell I. Inhibition by efferent nerve fibres: action on hair cells and afferent synaptic transmission in the lateral line canal organ of the burbot Lota lota. J Physiol. 1976 May;257(1):45–62. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel M., Seller H. Interaction of baroreceptor afferents from carotid sinus and aorta at the nucleus tractus solitarii. Pflugers Arch. 1970;318(1):7–20. doi: 10.1007/BF00588539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haymet B. T., McCloskey D. I. Baroreceptor and chemoreceptor influences on heart rate during the respiratory cycle in the dog. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;245(3):699–712. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton S. M. Hypothalamic control of the cardiovascular responses in fear and rage. Sci Basis Med Annu Rev. 1965:217–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan D., Spyer K. M. Is presynaptic inhibition responsible for suppression of the baroreceptor reflex during the defence reaction [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Oct;271(2):58P–59P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan D., Spyer K. M. Studies on the termination of sinus nerve afferents. Pflugers Arch. 1977 May 6;369(1):65–73. doi: 10.1007/BF00580812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan D., Spyer K. M. The excitability of sinus nerve afferent terminals during the respiratory cycle [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:66P–66P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOEPCHEN H. P., LUX H. D., WAGNER P. H. [Studies on time requirement and central development of the pressor receptor heart reflex]. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1961;273:413–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipski J., McAllen R. M., Spyer K. M. The carotid chemoreceptor input to the respiratory neurones of the nucleus of tractus solitarus. J Physiol. 1977 Aug;269(3):797–810. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipski J., McAllen R. M., Spyer K. M. The sinus nerve and baroreceptor input to the medulla of the cat. J Physiol. 1975 Sep;251(1):61–78. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllen R. M., Spyer K. M. The baroreceptor input to cardiac vagal motoneurones. J Physiol. 1978 Sep;282:365–374. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill E. G. Preliminary studies on nucleus retroambigualis-nucleus of the solitary tract interactions in cats. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(1):54P–55P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudomin P. Presynaptic inhibition induced by vagal afferent volleys. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Sep;30(5):964–981. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.5.964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT R. F. PHARMACOLOGICAL STUDIES ON THE PRIMARY AFFERENT DEPOLARIZATION OF THE TOAD SPINAL CORD. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1963 Jul 2;277:325–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00362515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sessle B. J. Excitatory and inhibitory inputs to single neurones in the solitary tract nucleus and adjacent reticular formation. Brain Res. 1973 Apr 27;53(2):319–331. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90217-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALL P. D. Excitability changes in afferent fibre terminations and their relation to slow potentials. J Physiol. 1958 Jun 18;142(1):1–21. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON M. F., CLARKE N. P., SMITH O. A., RUSHMER R. F. Interrelation between central and peripheral mechanisms regulating blood pressure. Circ Res. 1961 May;9:491–496. doi: 10.1161/01.res.9.3.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss G. K., Crill W. E. Carotid sinus nerve: primary afferent depolarization evoked by hypothalamic stimulation. Brain Res. 1969 Nov;16(1):269–272. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


