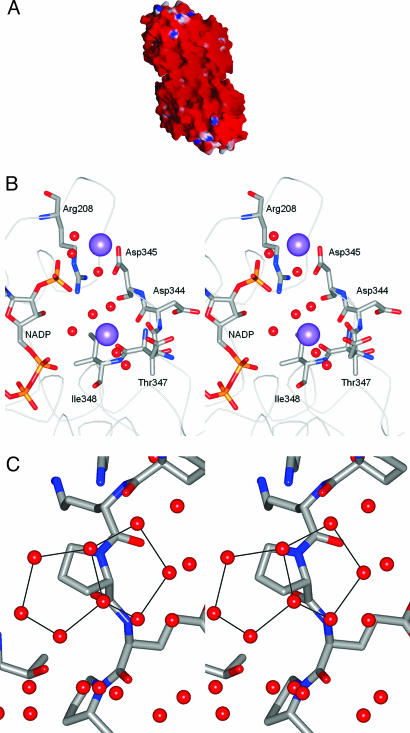
Fig. 1.
The Hm GlcDH structure. (A) The molecular surface of the dimer of Hm GlcDH to show the electrostatic potential calculated at 0 M salt concentration, prepared by using the program grasp (17, 18). Red corresponds to a surface potential less than −10 kcal(mol·electron)−1; blue corresponds to a potential greater than +10 kcal(mol·electron)−1. (B) Stereo view of the location of two of the potassium ions (lilac spheres). Individual residues are shown in atom colors if they lie within 3.5 Å of each potassium ion. The remainder of the polypeptide chain is shown as an alpha carbon trace, whereas water molecules are depicted as red spheres. The bound cofactor, NADP, can be seen to lie close to a cation cluster involving two bound counterions. (C) A close up stereo view, using standard atom coloring for the protein, to show two fused pentagonal rings suspended above the hydrophobic chain of proline 21 and anchored by hydrogen-bonding interactions to the surrounding water molecules and polar protein atoms.