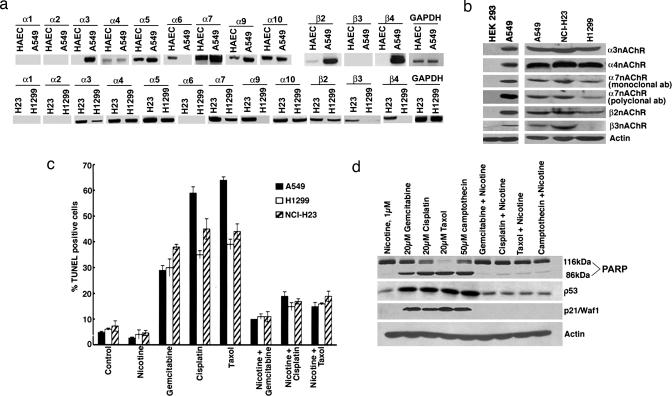
Fig. 1.
Nicotine inhibits drug-induced apoptosis in lung cancer cells. (a) RT-PCR showing the expression of nAChR subunits in A549, NCI-H23, and H1299 NSCLC cells. cDNA from human aortic endothelial cells was the positive control; PCR for GAPDH was used as the loading control. (b) nAChR protein expression in A549, NCI-H23, and H1299 cells as seen by Western blotting. Lysates from HEK293 cells were used as the negative control. (c) Nicotine inhibits apoptosis induced by chemotherapeutic drugs. Quiescent A549, NCI-H23, and H1299 cells were treated with 20 μM gemcitabine, cisplatin, or taxol; the presence of 1 μM nicotine inhibited apoptosis, as seen in a TUNEL assay. (d) A similar experiment as in c where apoptosis in A549 cells was assessed by PARP cleavage; although there was a significant amount of PARP cleavage in cells treated with the drugs, it was greatly reduced when nicotine was present. Induction of p53 and p21/Waf1/CIP1 by the drugs was also inhibited by nicotine.