Fig. 3.
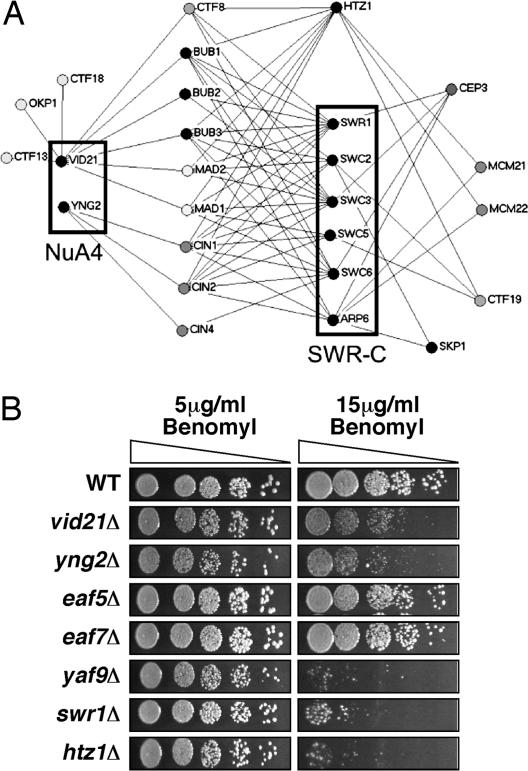
Htz1, SWR-C, and the NuA4 complex function to regulate chromosome stability/transmission. (A) SGA analysis (19) using either a transcription-targeted 384-deletion-strain array or genome-wide kinetochore screens (K.B. and V. Measday, unpublished data) identified numerous synthetic genetic interactions between deletions of genes encoding Htz1, SWR-C, or the NuA4 subunits Vid21 and Yng2, and known chromosome stability/transmission factors (see text for details). Genome-wide screens were carried out with four essential kinetochore genes [skp1–3 (42), cep3–1 (43), ctf13–30 (44), and okp1–5 (45)], whereas the nonessential components (mcm21Δ, mcm22Δ, ctf19Δ, bub1Δ, bub3Δ, mad1Δ, and mad2Δ) were present on the targeted miniarray. (B) Effects of the microtubule destabilizing agent benomyl on the growth of wild-type (NJK28), vid21Δ (NJK1042), eaf5Δ (NJK1259), eaf7Δ (NJK1254), yng2Δ (NJK1482), yaf9Δ (NJK1240), htz1Δ (NJK1527), and swr1Δ (NJK1665) strains. Five-fold serial dilutions of strains starting from an OD600 of 0.1 were plated onto yeast extract/peptone/dextrose plates containing 5 or 15 μg/ml benomyl and incubated for 2 days at 30°C.