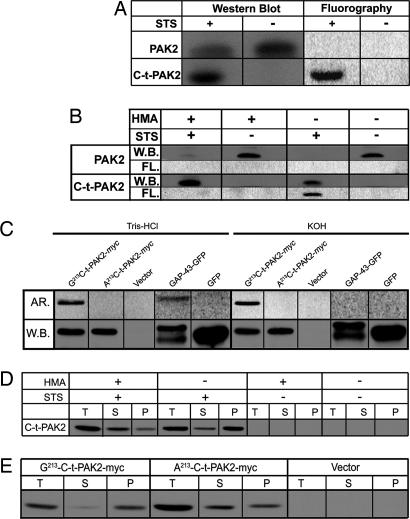
Fig. 1.
C-t-PAK2 is posttranslationally myristoylated on Gly-213 by NMT during apoptosis in Jurkat T cells. (A) Jurkat T cells were metabolically labeled with [9,10(n)-3H]myristate and incubated for 5 h in the absence or presence of 2.5 μM STS and 5 μg/ml cycloheximide (STS) to induce apoptosis. Cells were lysed, and PAK2 was immunoprecipitated. Immunocomplexes were analyzed by Western blotting (W.B.) and fluorography (FL). (B) Jurkat T cells were metabolically labeled and induced to undergo apoptosis as in A in the absence or presence of 1 mM HMA. Samples were analyzed as in A. (C) COS-7 cells were transfected with plasmids allowing expression of Gly-213-C-t-PAK2-myc, the nonmyristoylatable Ala-213-C-t-PAK2-myc chimeras, vector alone, a palmitoylatable (nonmyristoylated) chimeric GAP-43-GFP, or GFP. Transfected cells were metabolically labeled with [9,10(n)-3H]myristate or [125I]iodopalmitate for 4 h and lysed. Expressed proteins were immunoprecipitated and analyzed by Western blotting. PVDF membranes were then soaked for 24 h in either 0.2 M KOH or 1 M Tris·HCl (pH 7.0) and subjected to imaging with PhosphorImager screens (AR.). (D) Subcellular distribution of endogenous C-t-PAK2 in Jurkat T cells treated as in B were lysed and fractionated into total (T), cytosolic (S), and membrane (P) fractions. The presence of C-t-PAK2 was analyzed by Western blotting/enhanced chemiluminescence. (E) COS-7 cells were transfected with plasmids expressing Gly-213-C-t-PAK2-myc, the nonmyristoylatable Ala-213-C-t-PAK2-myc chimeras, or vector alone and were analyzed 12–14 h after transfection. Cells were subjected to subcellular fractionation and C-t-PAK2 detection as in D.