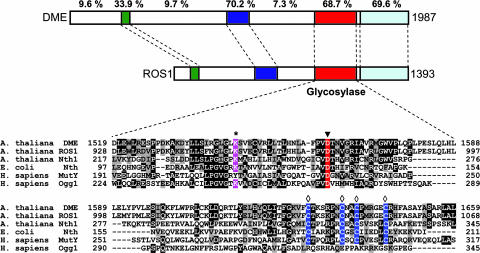
Fig. 1.
DME and ROS1 contain a DNA glycosylase domain and are closely related. (Upper) Diagram of DME and ROS1 showing the conserved domains as colored sections. The percentage of identical residues between both proteins is shown above each region. (Lower) Amino acid sequence alignment of DME (amino acids 1519–1659) and ROS1 (amino acids 928-1068) with A. thaliana Nth1, E. coli Nth, and Homo sapiens MutY and Ogg1. GenBank accession nos. are ABC61677, AAP37178, CAC16135, P20625, Q9UIF7, and O15527, respectively. An asterisk marks the lysine residue that is diagnostic of a glycosylase/lyase activity, the filled triangle indicates the conserved aspartic acid residue in the active site, and the open diamonds label the cysteine residues that in E. coli Nth1 ligate a [4Fe–4S] cluster.