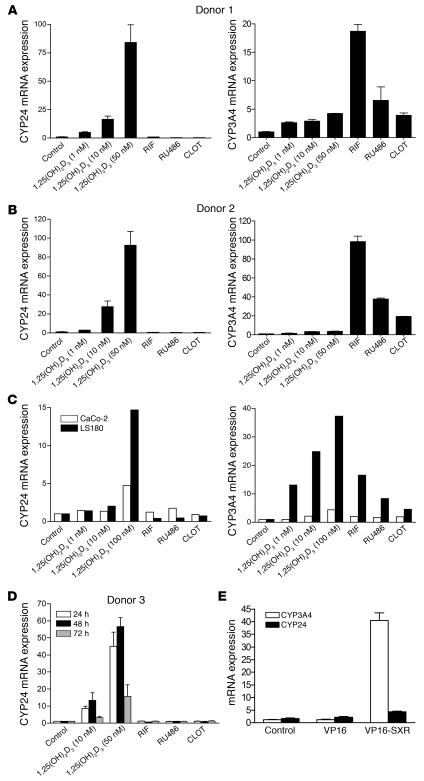
Figure 2. 1,25(OH)2 D3 but not SXR ligands induce CYP24 gene expression in human primary hepatocytes and intestinal cells.
(A and B) Human primary hepatocytes from 2 different donors were treated with 1, 10, or 50 nM of the VDR ligand 1,25(OH)2D3 or 10 μM of SXR ligands RIF, CLOT, or RU486 for 24 hours as indicated. Total RNA from each sample was isolated, and the expression of CYP3A4 and CYP24 genes was determined by QRT-PCR assays. (C) Two different immortalized human intestinal cell lines, Caco-2 and LS180, were treated with 1, 10, or 100 nM of the VDR ligand 1,25(OH)2D3 or 10 μM of SXR ligands RIF, CLOT, or RU486 for 24 hours as indicated. Total RNA from each sample was isolated, and the expression of CYP3A4 and CYP24 genes was determined by QRT-PCR assays. (D) Human primary hepatocytes from donor 3 were treated with 10 or 50 nM of the VDR ligand 1,25(OH)2D3 or 10 μM of SXR ligands RIF, CLOT, or RU486 for 24, 48, or 72 hours as indicated. Total RNA from each sample was isolated, and the expression of CYP24 genes was determined by QRT-PCR assays. (E) LS180 cells were transfected with control vector, VP16, or VP16-SXR expression vector; total RNA from each sample was isolated; and the expression of CYP3A4 and CYP24 genes was determined by QRT-PCR assays.