Table 3.
Summary of Inequality Indicators Evaluated for Health Benefits Analysis.
| Gini index | Variance of logarithms | Squared coefficient of variation | Atkinson index | Mean log deviation | Theil's entropy index | |
| Formula |
|
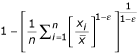 where ε = inequality aversion (range from 0 to infinity) where ε = inequality aversion (range from 0 to infinity) |
||||
| Approach for comparisons | Relative to all those better off | Relative to the average | Relative to the average | Relative to the average | Relative to the average | Relative to the average |
| Method for aggregation | Additive | Weighted additive | Weighted additive | Weighted additive | Weighted additive | Weighted additive |
| Principle of transfers? | Y | N (fails for transfers at high levels) | N (fails for transfers at high levels) | Y | Y | Y |
| Subgroup decomposable in standard form? | N (unless subgroups strictly ordered by income) | N | Y (within-group and between-group not independent) | Y (although not strictly additive) | Y | Y |
| Avoids value judgment about weights? | N (in standard application; extended Gini can address) | N | N | Y | N | N |
| Conclusions | Rejected as stand- alone indicator; potentially useful for sensitivity analyses | Rejected | Rejected | Accepted | Rejected as stand-alone indicator; useful in combination with other indicators | Rejected as stand-alone indicator; useful in combination with other indicators |
