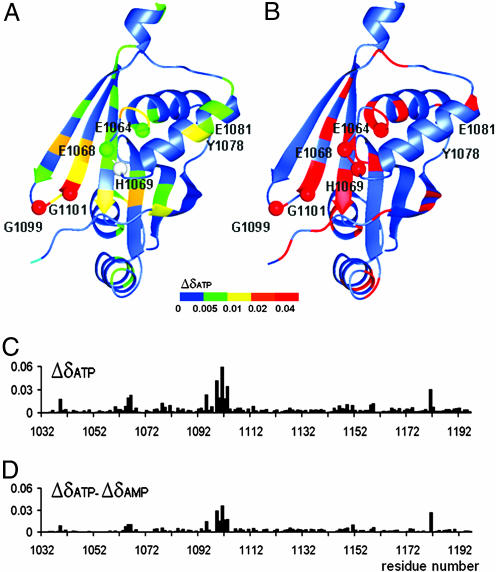
Fig. 4.
Residues affected by nucleotide binding and the location of Wilson disease-causing mutations. (A) The structure of the ATP7B N-domain with a color map of backbone amide chemical shift changes induced by ATP binding. The secondary chemical shifts for each residue are expressed as Δδ = (((δHNNUC − δHNfree)/δHNNUC)2 + ((δNNUC − δNfree)/δNNUC)2)1/2, where δHNNUC and δNNUC are 1H and 15N chemical shifts of the backbone amide group in the presence of the nucleotide, and δHNfree and δNfree are chemical shifts measured without nucleotide present. Data for H1069 (gray) is not available. The residues invariant in the P1B-ATPases are shown as spheres. The disordered loop A1114-T1143 is not shown. (B) The location of disease causing mutations is shown in red. (C) Chemical shift changes (Δδ, defined above) at each amino acid residue upon binding of ATP. (D) Chemical shift changes at each residue observed on binding ATP minus the corresponding chemical shift changes on binding AMP.