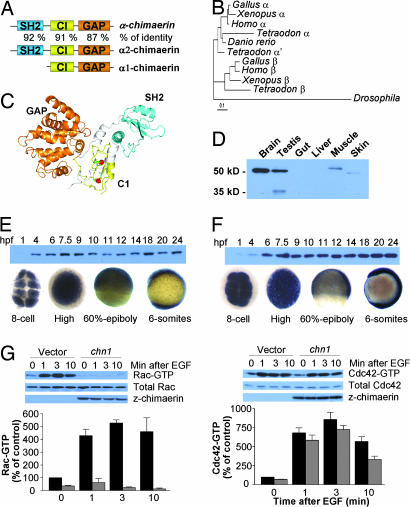
Fig. 1.
α-chimerin is a Rac-GAP that is zygotycally and maternally expressed in zebrafish. (A) Structure of chn1 and identity to α-chimerins. (B) Phylogenetic analysis of chimerin genes. (C) Molecular modeling of chn1. Cyan, SH2 domain; yellow, C1 domain; orange, GAP domain. (D) Western blot showing the expression of chn1 in different adult zebrafish organs. (E and F) Expression of chn1 and z-Rac in the zebrafish embryo at different stages by Western blot (Upper) and in situ hybridization (Lower). (G) Determination of Rac-GTP and Cdc42-GTP levels in COS-1 cells transfected with either pcDNA3-HA-chn1 (black bars) or pcDNA3-HA (empty vector; gray bars). Forty-eight hours after transfection, cells were serum starved (18 h) and then stimulated with EGF (100 ng/ml) for the times indicated in the figure. Rac-GTP and Cdc42-GTP levels were determined by using a pull-down assay, as described in Materials and Methods. Representative Western blots are included. Densitometric analysis of Rac-GTP and Cdc42-GTP levels normalized to total levels in each case is presented. Data are expressed percentage relative to Rac-GTP or Cdc42-GTP levels before EGF stimulation and represent the mean ± SE of five independent assays.