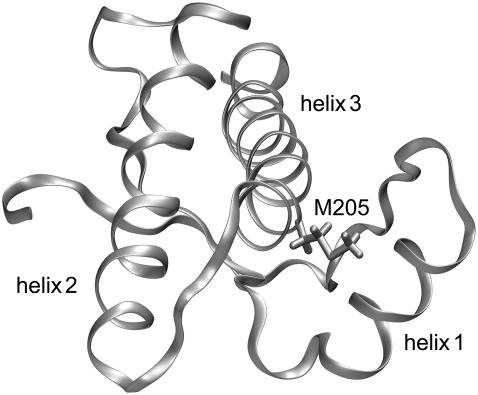
FIGURE 1.
Backbone folding pattern of the human prion protein in the C-terminal domain (residues 125–228) according to the NMR structure in Zahn et al. (3). Besides a two-stranded antiparallel β-sheet, the structure comprises three α-helices, helix 1 (144–154), helix 2 (173–194), and helix 3 (200–228). Also drawn is the hydrophobic side chain of methionine 205, which is part of helix 3. According to the figure, this side chain is buried in the contact region between helix 3 and helix 1. This structural arrangement suggests that the replacement of M205 by a hydrophilic residue like serine or arginine could induce an intrusion of water molecules into the contact region and, thus, loosen the attachment of the two helices.