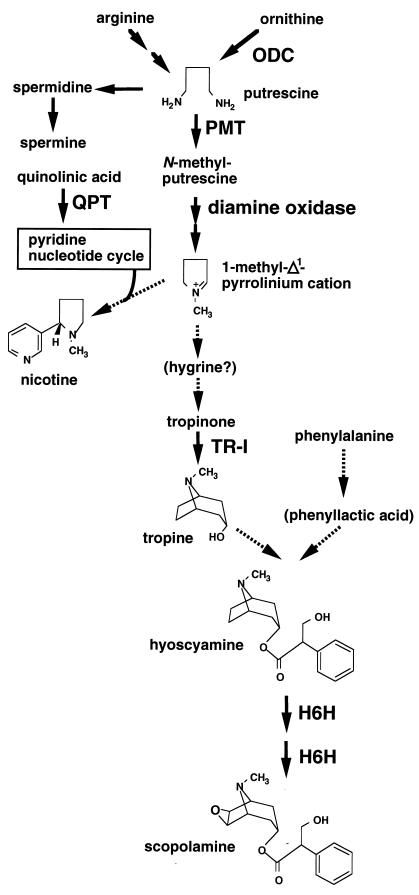
Figure 1.
Biosynthetic pathways of tropane alkaloids and nicotine. Tropane alkaloids and nicotine are derived from diamine putrescine produced from ornithine by ornithine decarboxylase (ODC), arginine, or both (28, 29). Putrescine is N-methylated by PMT then oxidatively deaminated by diamine oxidase to the 1-methyl-Δ1-pyrrolinium cation (30). This cation is condensed with a derivative of nicotinic acid, forming nicotine in tobacco, or is further metabolized to tropinone in tropane alkaloid-producing plants. Hygrine is formed nonenzymatically by condensation of the cation and acetoacetic acid (31), but its involvement in alkaloid biosynthesis has not been established. Tropinone is reduced by tropinone reductase I (TR-I) to tropine (22), which condenses with phenyllactic acid or its derivative, giving hyoscyamine. Scopolamine is formed from hyoscyamine via 6β-hydroxyhyoscyamine by the bifunctional enzyme hyoscyamine 6β-hydroxylase (H6H) (32). The nicotinic acid moiety of nicotine is supplied from the pyridine nucleotide cycle, in which quinolinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase (QPT) serves as the entry-point enzyme.