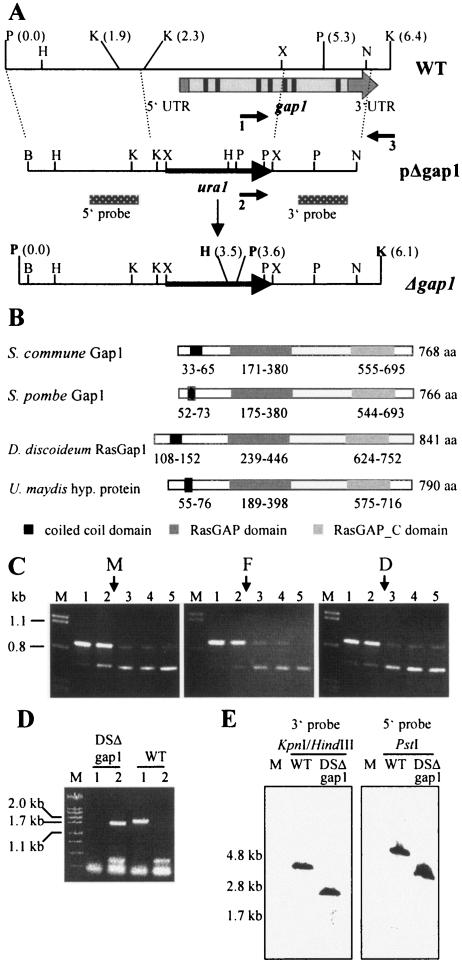
FIG. 3.
Sequence and expression analyses of gap1 and deletion strategy. (A) Restriction map of the genomic region of strain W21 harboring the gap1 gene (WT). The relative position of gap1 is indicated by the arrow. The cDNA of gap1 contains 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions (UTR) and seven introns (indicated in black) and eight exons (shown in light gray). Homologous recombination of the deletion construct (pΔgap1) leads to replacement of the 5′ part of gap1 by the ura1gene (Δgap1). The positions of primers used to identify the disruption mutant DSΔgap1 are indicated by arrows (1, gap1_del; 2, ura1_del; and 3, gap3′1_del). Location of probes 5′ and 3′ are shown by the dotted bars. The new restriction sites BamHI and XbaI in pΔgap1 were introduced during cloning and were used together with the existing XbaI and NdeI sites for construction of pΔgap1. B, BamHI; H, HindIII; K, KpnI; N, NdeI; P, PstI; X, XbaI. (B) Domain structures of Gap1 from S. commune and its homologues. Numbers represent the amino acid (aa) positions of each domain. Domain annotations: RasGAP, (smart) SM00323; RasGAP_C, (pfam)PF03836. Accession numbers: ScGap1, AAT74386.1; SpGap1, A40258; DdRasGap1, AAB39262.1; U. maydis hypothetical protein, UM00949.1 and EAK81710.1. (C) Expression of gap1 in monokaryon 4-39 (subpanel M), common A heterokaryon 4-39 × W21 (flat, subpanel F), and dikaryon 4-39 × 4-40 (subpanel D) of S. commune grown for 3 days in CYM liquid medium. A total of 10 ng of cDNA was used in each PCR. Competitive PCR led to coamplification of the gap1 cDNA fragment (680 bp) and the competitor fragment (870 bp). Arrows indicate the estimated equimolar concentrations of target and competitor fragments. Lanes: M, λ-DNA cut with PstI; 1, 1.35 × 10−6 fmol (813 molecules); 2, 6.9 × 10−7 fmol (416 molecules); 3, 3.5 × 10−7 fmol (211 molecules); 4, 1.8 × 10−7 fmol (108 molecules); 5, 9.1 × 10−8 fmol (55 molecules) competitor used in the reaction. (D) Agarose gel electrophoresis of PCR products that led to identification of DSΔgap1. Genomic DNA of strains indicated was used in the reactions. Lanes: M, λ-DNA cut with PstI; 1, primers 1 and 3; 2, primers 2 and 3 were used in the reaction. See panel A for primer names. WT, wild-type strain. (E) Southern blot analysis to confirm single, homologous integration of pΔgap1. Genomic DNA of wild-type strain (DSII-1) and strain DSΔgap1 was cut with the enzyme(s) indicated and hybridized to the 3′ and 5′ probe, respectively. Expected fragment sizes can be deduced from panel A.