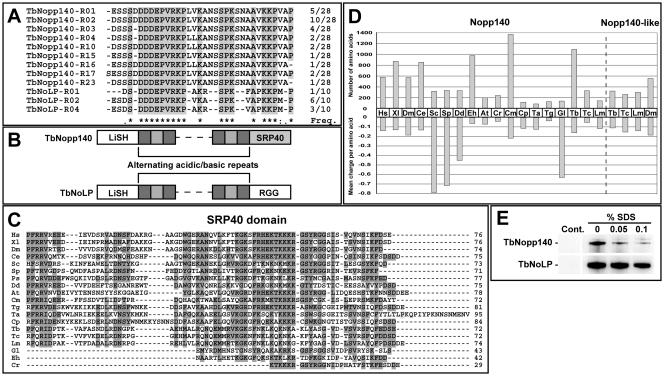
FIG. 1.
Properties of Nopp140 proteins. (A) Alignment of all central domain repeats from TbNopp140 and TbNoLP. (B) Domain diagram of TbNopp140 and TbNoLP. (C) Alignment of SRP40 domain across a broad range of eukaryotes: Hs, Homo sapiens; Xl, Xenopus laevis; Dm, Drosophila melanogaster; Ce, Caenorhabditis elegans; Sc, Saccharomyces cerevisiae; Sp, Schizosaccharomyces pombe; Ps, Phytophthora sojae; Dd, Dictyostelium discoideum; At, Arabidopsis thaliana; Cm, Cyanidioschyzon merolae; Tg, Toxoplasma gondii; Ta, Theileria annulata; Cp, Cryptosporidium parvum; Tb, Trypanosoma brucei; Tc, Trypanosoma cruzi; Lm, Leishmania major; Gl, Giardia lamblia; Eh, Entamoeba histolytica; and Cr, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. (D) Comparison between central domain size and mean charge per amino for Nopp140 and Nopp140-like proteins in the same set of organisms. (E) Immunoprecipitates from 108 cells extracted in RIPA buffer with the addition of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS; as indicated), and detected with the NUMAG monoclonal antibody. A Pol I-specific monoclonal was used (lanes 2 to 4) along with an unrelated control (Cont.; lane 1).