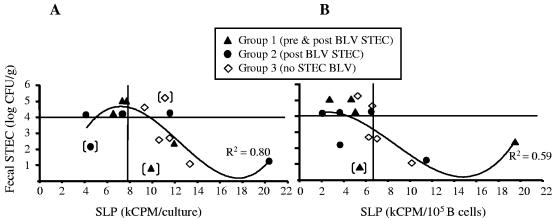
FIG. 5.
Suppression of BLV-induced SLP correlated with the total numbers of fecal STEC bacteria. Three experimental groups are shown that were treated biweekly with oral doses of 5 × 1010 CFU bacteria/animal. Two groups received STEC, starting 2 weeks before BLV challenge (pre & post BLV STEC, group 1) or starting 24 h post-BLV challenge (post BLV STEC, group 2) and continuing for 16 weeks post-BLV challenge. The infection control group (BLV no STEC, group 3) received E. coli K-12 starting at week −2. All three groups were challenged with BLV. Fecal STEC counts, averaged over a 2-month period post-BLV challenge and expressed as the logs of CFU/g, are plotted against kCPM per culture (A) or against kCPM per 105 B cells in culture (B). Horizontal solid lines at log 4 separate CFU counts considered high (above log 4) and those considered low (below log 4). Vertical lines indicate the upper ranges of background SLP in the healthy control group. Data points were fitted with cuboidal polynomial lines (R2 values shown) after the exclusion of outliers with fecal STEC numbers inconsistent with treatment (points in brackets).