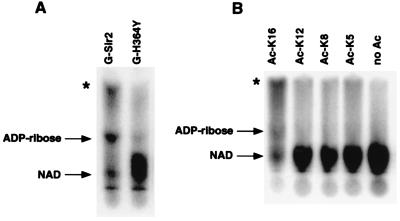
Figure 1.
Acetyl-lysine-dependent NAD breakdown by Sir2: autoradiographs of TLC plates used to separate labeled reaction products. Arrows indicate the migration positions of cold standards. Asterisks denote product 2. (A) Stimulation of NAD breakdown by calf thymus histones. Reactions contained 5 μCi [32P]NAD (1 μM final concentration) and either wild-type Sir2 (G-Sir2) or the H364Y point mutant (G-H364Y). Incubations were for 6 h at 25°C. (B) Stimulation of NAD breakdown by histone H4 N-terminal peptides. Reactions contained 5 μCi [32P]NAD, 100 μM cold NAD, 500 μM peptide acetylated at the indicated lysine, and wild-type Sir2. Incubations were for 6 h at 25°C.