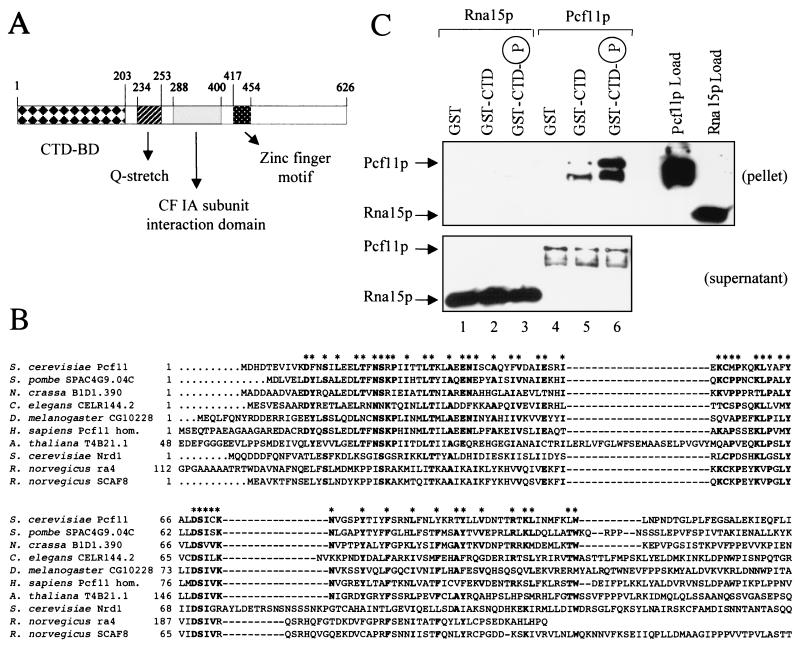
Figure 2.
Pcf11p contains a CTD-binding domain and interacts directly with the CTD. (A) Schematic representation of the domain organization of Pcf11p. The CTD-binding domain is indicated as CTD-BD. (B) Alignment of conserved CTD-binding domains. The N-terminal CTD-binding domain of S. cerevisiae Pcf11p is compared with domains of homologous proteins from S. pombe (SPAC4G9.04C gene product; GenBank accession no. Z69727), Neurospora crassa (B1D1.390 gene product; no. CAB91288), C. elegans (CELR144.2 gene product; no. U23515), Drosophila melanogaster (CG10228 gene product; no. AAF58192), Homo sapiens (Pcf11 homolog; no. AF046935), Arabidopsis thaliana (T4B21.1 gene product; no. AAD03447), S. cerevisiae Nrd1p (no. CAA96158), Rattus norvegicus rA4 (no. U49058), and R. norvegicus SCAF8 (no. U49055). Bold residues indicated with asterisks are identical among at least five of the sequences. In addition to these residues, there are many similarities that are not highlighted. The gaps introduced to maximize the homology are represented by dashed lines. (C) Pcf11p interacts directly with the CTD, whereas Rna15p does not. Recombinant His-tagged Pcf11p and Rna15p were chromatographed on GST, GST-CTD, and phosphorylated GST-CTD resins. The bound fraction was eluted with SDS sample buffer and detected by Western blot with antihistidine monoclonal antibodies. Load (100% of input), pellet (100%), and supernatant (10%) fractions are shown. Lanes 1–3, Rna15p chromatography; lanes 4–6, Pcf11p chromatography. The lower bands detectable in lanes 5 and 6 are degradation products of full-length Pcf11p.