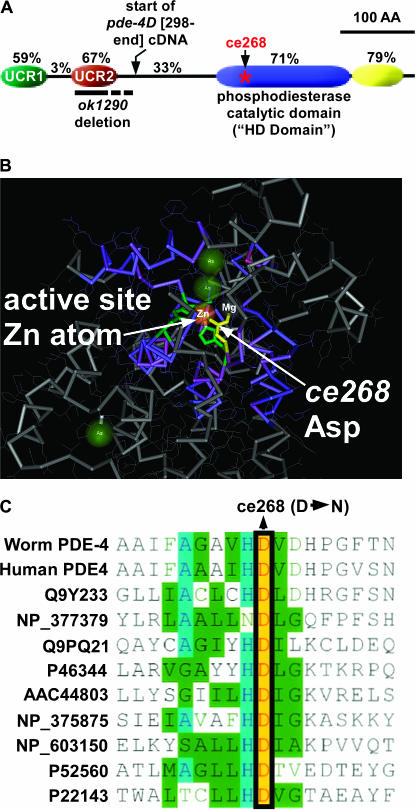
Figure 4.
Conserved PDE-4 domains and mutation locations. (A) A drawing of C. elegans PDE-4 highlighting four conserved domains. Percentages indicate the percentage identity to human phosphodiesterase 4D (NP_006194). Locations of the ce268 mutation and the ok1290 deletion are indicated. The dashed line at the right half of the ok1290 deletion indicates uncertainty about which cryptic splice site(s) are used at the ok1290 mutant locus (see text). The drawing begins with Arg 117 of the PDE-4D isoform (this is the beginning of exon 2 of the D isoform, sequence context RRESFLYR) and does not include N-terminal sequences that vary between the five predicted products the pde-4 locus. A previous comparison of Drosophila and human PDE-4D identified and named the upstream conserved regions (UCR1 and UCR2) (Bolger et al. 1993). Domain boundaries relative to the PDE-4D isoform are as follows: UCR1 (R117–N179), UCR2 (A211–K274), catalytic domain (Y406–W588), and C-terminal conserved domain (R589–P658). The boundaries of the catalytic HD domain were identified using the National Center for Biotechnology Information Conserved Domain Search tool (Marchler-Bauer et al. 2005) during a BLASTP search using the PDE-4D isoform. The PDE-4D protein sequence used for this analysis is taken from WormBase, WS 149 (Chen et al. 2005). (B) The crystal structure of the catalytic domain of human PDE4 as determined by Hatley et al. (2000). The Asp that is mutated in pde-4(ce268) is yellow. Note that this residue participates in coordinating a zinc atom as well as a second metal ion that is probably a magnesium atom (Hatley et al. 2000). Other residues that coordinate the zinc atom are partially visible and green. This image was exported from Cn3D version 4.1 (National Center for Biotechnology Information). (C) An amino acid alignment of various metal-dependent phosphodiesterases in the region around the ce268 mutation. The alignment includes human phosphodiesterase 4, other cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases, and distantly related bacterial phosphodiesterases that are not involved in cyclic nucleotide metabolism. Accession numbers (left column) can be used for details on the source of each sequence.