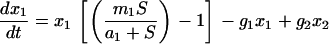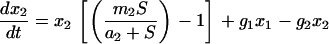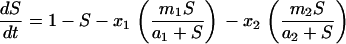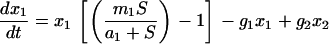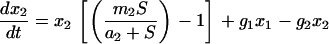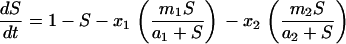A model of two subpopulations competing in the chemostat:
The cells are assumed to have two metabolic states, 1 and 2, with different Monod growth kinetics (
Smith and Waltman 1995) (parameters
m1,
a1 and
m2,
a2, respectively). State 2 is assumed to be better fitted to a new environment introduced at
t = 0. At this environment, state 2 cells can maintain the growth rate dictated by the chemostat with a lower concentration of limiting nutrient and a higher cell concentration.
x1 and
x2 are concentrations of cells in the two populations,
S is the concentration of limiting nutrient in the chemostat, and
g1 is the rate of metabolic switch between state 1 and state 2 while
g2 is the switching rate in the opposite direction. The equations are normalized: time in units of the chemostat dilution rate (normalizing also
m and
g) and all concentrations are in units of the limiting nutrient concentration in the feeding solution.
x1 and
x2 are normalized additionally by their respective yields (ratio of biomass to nutrient). The model is computed in two forms: (1) setting initial value
x2(
t = 0) = 0 and
g1,2 ≠ 0 to compute the population dynamics following a medium switch, from
m1 and
a1, unfavorable metabolism (causing a reduction in
x1), to
m2 and
a2—favorable metabolism in the new medium (causing
x2 to overtake the population) (black curve,
g1 = 10
−7,
g2 = 0.2; red curve,
g1 = 10
−20,
g2 = 0.2); (2) setting an initial value of
x2 as a fraction of the total population (10%) and
g1,2 = 0 to compute the dynamics of a genetically heterogeneous population competing in the chemostat [
x1(
t = 0) = 0.7 and
x2(
t = 0) = 0.07, green curve]. Note that in this case, the fast exponential increase of the population forces a short adaptation duration, which is inconsistent with the experimental results. All other parameters are the same for all computations:
m1 = 1.14,
m2 = 1.65,
a1 = 0.11,
a2 = 0.019.