Figure 3.
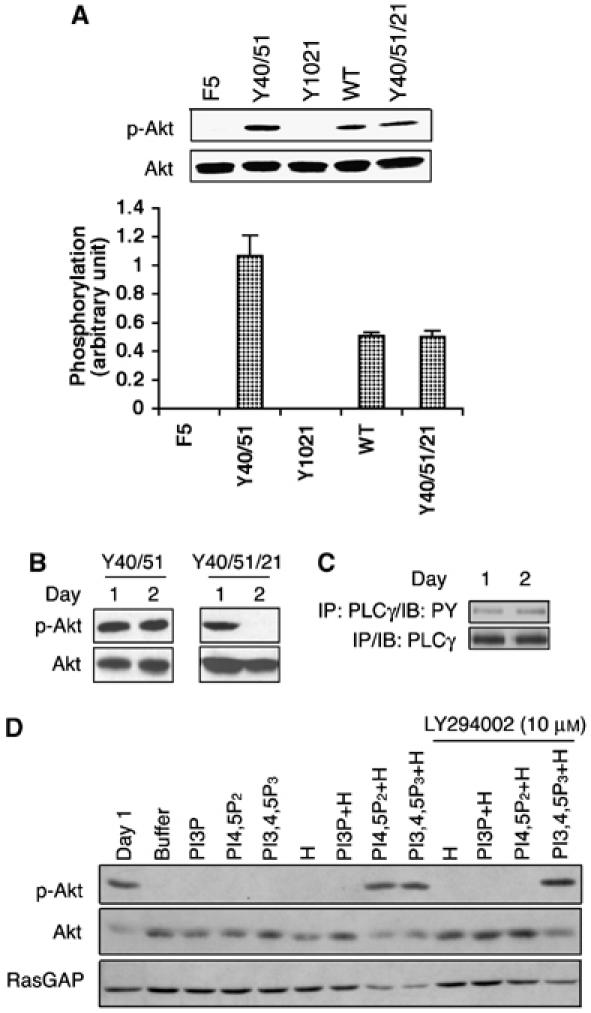
(A) Recruiting PLCγ attenuated activation of Akt. Monolayers of cells expressing the indicated receptors were stimulated with 100 ng/ml PDGF for 5 min. The cells were harvested and total cell lysates were subjected to a Western blot using an anti-phosphoAkt (Ser473) antibody. The blot was then stripped and reprobed with an anti-Akt antibody. The bar graph shows the ratio of the phosphoAkt/Akt signal; the error bars are standard deviation of three independent experiments. (B) Activation of PLCγ correlated with a decline in phosphoAkt. BRECs expressing the indicated receptor were organized into tubes as described in the legend of Figure 1. At the desired times, total cell lysates were made and subjected to Western blot analysis using anti-phosphoAkt (Ser473) and anti-Akt antibodies. (C) Phosphotyrosine of PLCγ did not change when tubes regressed in the Y40/51/21 cells. The Y40/51/21 cells were subjected to a tube assay. At the indicated times, total cell lysates were made, immunoprecipitated with a PLCγ antibody and the phosphotyrosine content of PLCγ was assessed by Western blot analysis using an anti-phosphotyrosine antibody. (D) Synthetic lipids restored the level of phosphoAkt. The Y40/51/21 cells were subjected to a tube assay. Synthetic lipids and/or histone (H) were added every 12 h beginning at 12 h and ending at 48 h. For the treatment of LY294002 (10 μM), a mixture of synthetic lipids and histone was added with LY294002 simultaneously. Total lysates were made and subjected to Western blot analysis using anti-phosphoAkt and anti-Akt antibodies. The blot was stripped and reprobed with RasGAP as a loading control.
