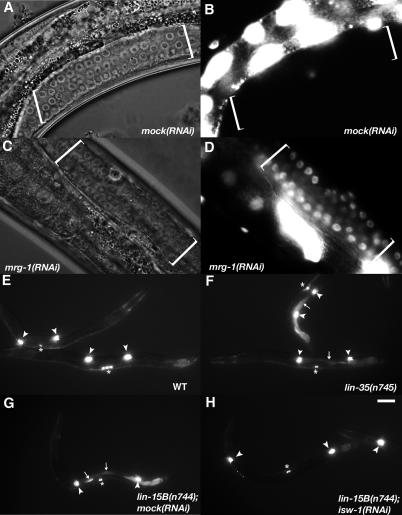
Figure 5. The SynMuv Suppressor Genes Are Required for Germline Transgene Silencing in WT Animals and for the lag-2::gfp Ectopic Expression in lin-15B(n744) .
(A–D) DIC (A) and (C) and GFP fluorescence (B) and (D) images of hermaphrodite germline from transgenic strain PD7271 that contains the multicopy let-858::gfp reporters [75]. Brackets indicate the region of germ cell nuclei. The transgene was silenced in WT, but desilenced in animals treated with mrg-1(RNAi). RNAi of seven other SynMuv suppressors also displayed a similar effect (Table 3). Bar: 10 μm.
(E–H) GFP fluorescence images of mid-L4 larvae carrying the lag-2::gfp transgene. (E) WT animals display a strong expression of the transgene in distal tip cells (arrowheads) and the vulva (asterisks). (F–G) a strong ectopic expression of the transgene in the intestine (arrows) is seen in two SynMuv mutants. (H) RNAi of isw-1 suppressed the ectopic expression of lag-2::gfp in the intestine of the lin-15B(n744) mutant, but not its expression in distal tip cells and vulval cells. RNAi of 14 other SynMuv suppressors also displayed a similar effect (Table 3). Bar: 100 μm.