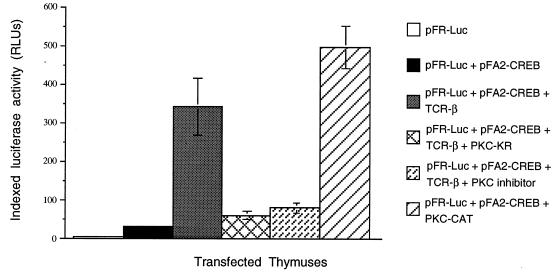
Figure 2.
PKC is activated downstream of preTCR complex formation. The activation of PKC-mediated pathways was determined by a previously described reporter plasmid system (see ref. 23). The reporter plasmid system utilizes two plasmids: (i) a fusion activator plasmid (pFA2-CREB) that encodes a transactivation domain of CREB (residues 1–280) fused with the GAL4 DNA-binding domain) and (ii) a luciferase reporter plasmid (pFR-Luc), which encodes a luciferase gene under the control of five GAL4-binding elements. Therefore, phosphorylation/activation of CREB by an upstream kinase, such as PKC, can be monitored in the form of luciferase activity. RAG° fetal thymuses were gene gun-transfected with pFR-Luc (DLR = 250 ng) and CMV-β-gal (DLR = 250 ng) and either pFA2-CREB (DLR = 75 ng) alone or together with TCR-β (DLR = 250 ng), TCR-β and dominant-negative PKC (PKC-KR; DLR = 750 ng), or TCR-β and treated with PKC-specific inhibitor bisindolylmaleimide (1 μM) or constitutively active PKC (PKC-CAT; DLR = 250 ng), as indicated. The transfected lobes were then cultured for 16–20 h. Cells were then lysed, and the lysates were assayed for luciferase and β-galactosidase activity. The data shown are an average of at least four independent experiments. The individual luciferase activities were indexed against the observed β-galactosidase activity.