Figure 7. Bath application of adenylate cyclase activators enhances retinal firing but maintains appropriate features for driving eye-specific segregation.
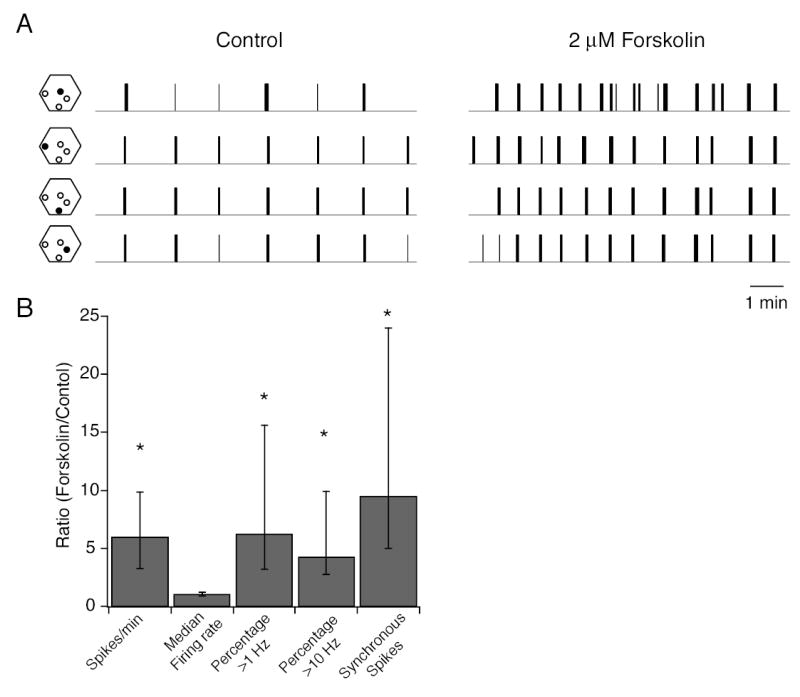
A. Spikes trains of 4 different neurons from a P4-5 WT retina in the absence (left) and presence (right) of 2 μM forskolin. Hexagons to the left of each spike train show the position (filled circle) of the electrode on the multielectrode array that recorded spikes. Total length of control and drug application recordings is 20 minutes.
B. Summary of effects of forskolin (2 μM) on the spike train parameters defined in Figures 5 and 6. Data is presented as a ratio of the value of a parameter in the presence of forskolin normalized to its value in control solutions. This ratio was computed for each cell in the population; data was respresented as medians and quartiles. n= 24 cells, 2 retinas for first 4 columns and n = 25 pairs, 2 retina for the number of syncrhonized spikes. Significance was assayed by a Wilcoxon signed rank test comparing control to forskolin for each parameter.
