FIG. 1. Molecular structure of intact cytoplasmic dynein.
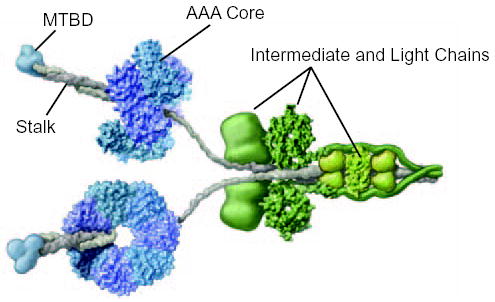
The cytoplasmic dynein motor is a dimer containing two identical heavy chain subunits of Mm ~520 kDa. The core of the motor, formed by the C-terminal two-thirds of the heavy chain, comprises a ring of six AAA ATPase domains, depicted here in blue and purple. The microtubule-binding domain (MTBD) (blue) protrudes from the AAA core on a coiled coil stalk (grey). The attachment of cargo to the dynein motor involves light and intermediate chain subunits (green) that are associated with the N-terminal third of the heavy chain. Adapted from (2) with permission.
